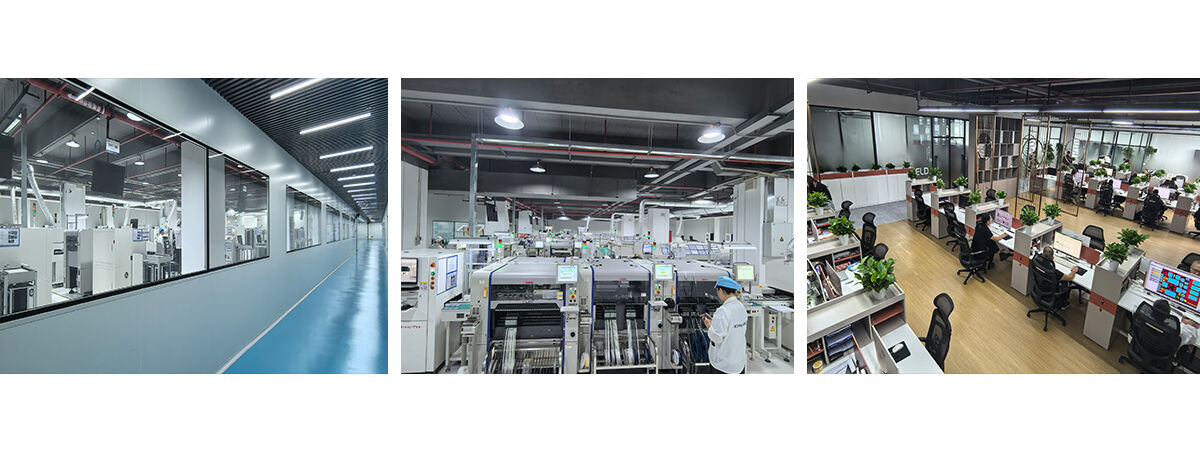
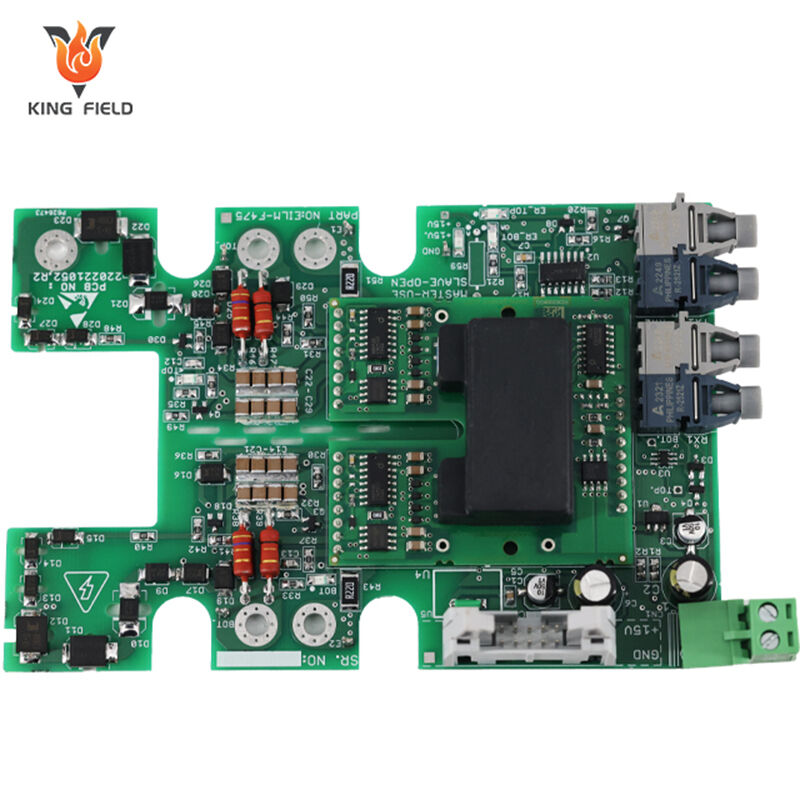
SMT Assembly Capabilities
Precision SMT Assembly for medical/industrial/automotive/consumer electronics—supports 01005 components, 0.4mm pitch, BGA/QFP. IPC-A-610 compliant, with AOI/ICT/X-ray testing, 24h prototyping, high-volume production & one-stop PCB+SMT integration.
✅ Ultra-fine-pitch & complex component placement
✅ IPC-A-610 compliance + strict quality checks
✅ One-stop PCB+SMT turnkey solution
Description
SMT Assembly Capabilities
SMT Assembly Capabilities refers to the surface mount technology assembly capabilities, which represent the comprehensive technical strength of an SMT factory or service provider in PCB manufacturing, encompassing processes, equipment, testing, production capacity, and quality control. It determines the yield, reliability, and production efficiency of assembled boards, covering the entire delivery process from prototyping to mass production.
SMT Assembly is a core electronic manufacturing process where surface mount devices (SMDs) – tiny components like resistors, capacitors, ICs, and sensors – are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB), rather than through holes. It is the dominant assembly method for modern electronic products due to its efficiency, miniaturization, and high-density capabilities.

Core Characteristics of SMT Assembly
Component Type: Uses SMDs, which are smaller and lighter than through-hole components.
Mounting Method: Components are placed on the PCB’s surface and soldered to pre-deposited solder paste on conductive pads, rather than inserting leads through PCB holes.
Automation-Driven: Relies on high-speed pick-and-place machines, stencil printers, and reflow ovens for mass production, ensuring precision and consistency.
Density & Miniaturization: Enables higher component density, critical for compact devices.
Key SMT Assembly Process Steps
Stencil Printing: A metal stencil with cutouts matching PCB pads is used to deposit solder paste onto the pads – ensures accurate solder placement.
Component Placement: Automated pick-and-place machines use vacuum nozzles to pick SMDs from reels/trays and place them precisely onto the solder paste-coated pads.
Reflow Soldering: The PCB is passed through a reflow oven with controlled temperature zones (preheat → soak → reflow → cool), melting the solder paste to bond components to the PCB; flux prevents oxidation and ensures proper wetting.
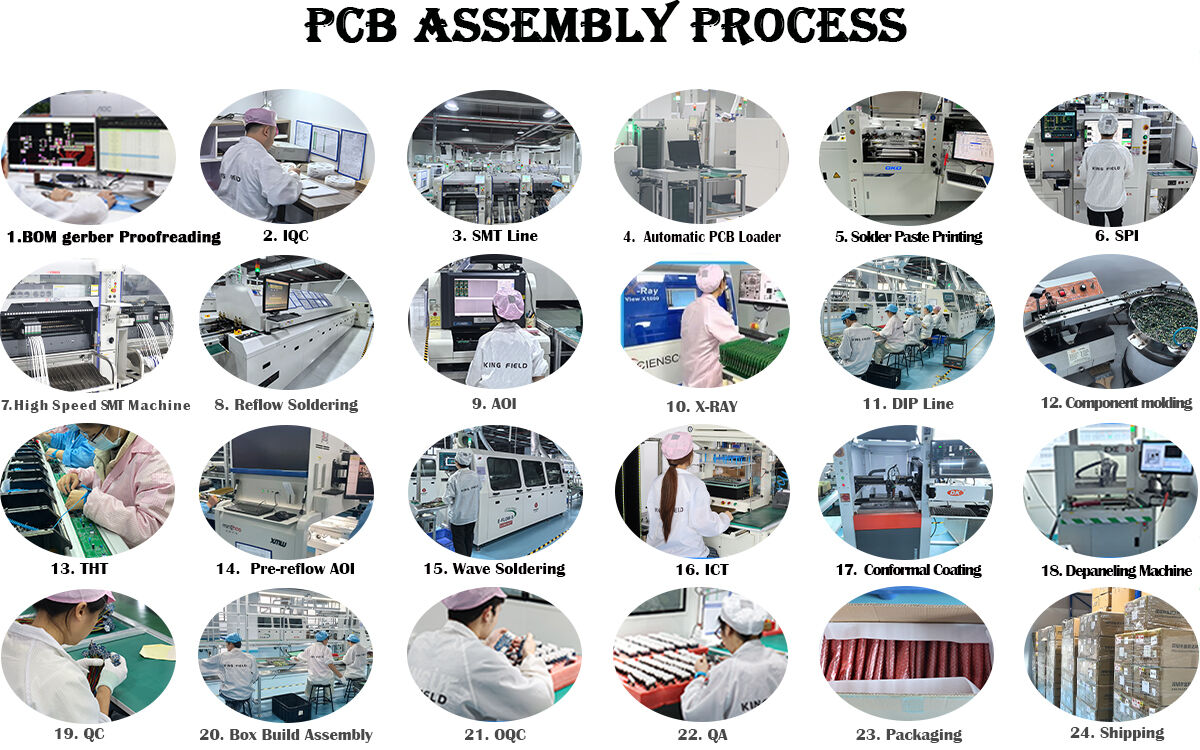
Inspection & Testing:
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection): Scans the PCB to detect defects.
X-Ray Inspection: For hidden defects.
Functional Testing: Verifies the assembled PCB performs to specifications.
Rework/Repair: Corrects defects if detected during inspection.

Advantages of SMT Assembly
Miniaturization: Enables smaller, lighter electronic devices (critical for consumer electronics, medical wearables).
High Production Efficiency: Automated processes support high-volume manufacturing with fast cycle times.
Cost-Effective: Lower material waste and labor costs compared to THT for mass production.
Improved Performance: Shorter electrical paths reduce signal delay and EMI, enhancing reliability (ideal for high-frequency applications like industrial control systems, automotive infotainment).
Dual-Side Mounting: Components can be placed on both sides of the PCB, maximizing space utilization.
Industry-Specific Applications
| Industry | SMT Assembly Use Cases | ||||
| Medical | PCBs for patient monitors, diagnostic equipment, wearable medical devices – requires high precision and compliance with ISO 13485. | ||||
| Industrial Control | PLCs, robotic control boards, sensor modules – durable, high-temperature resistant, and compliant with IEC 60335. | ||||
| Automotive | ECUs (engine control units), infotainment systems, ADAS components – meets IATF 16949 standards, withstands vibration/temperature extremes. | ||||
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, laptops, home appliances, IoT devices – high-density, miniaturized PCBs for compact designs. | ||||
SMT vs. Through-Hole Technology (THT)
| Aspect | SMT Assembly | THT Assembly | |||
| Component Size | Small (SMDs) | Larger (through-hole components) | |||
| Mounting Location | PCB surface (top/bottom) | Through PCB holes (leads on opposite side) | |||
| Production Speed | Fast (automated) | Slow (semi-automated/manual) | |||
| Mechanical Strength | Lower (better for low-vibration environments) | Higher (ideal for connectors, high-stress applications) | |||
| Typical Applications | Consumer electronics, medical wearables | Power supplies, industrial connectors | |||
Production Capacity
| Assembly Types |
● SMT Assembly( with AOI inspection); ● BGA Assembly(with X-Ray inspection); ● Through-hole Assembly; ● SMT & Through-hole Mixed Assembly; ● Kit Assembly |
||||
| Quality Inspection |
● AOI Inspection; ● X-Ray Inspection; ● Voltage Test; ● Chip Programming; ● ICT Test; Functional Test |
||||
| PCB Types | Rigid PCB、Metal core PCB、Flex PCB、Rigid-Flex PCB | ||||
| Component Types |
● Passives, smallest size 0201(inch) ● Fine-pitch chips to 0.38mm ● BGA (0.2mm pitch), FPGA, LGA, DFN,QFN with X-Ray testing ● Connectors and terminals |
||||
| Components Sourcing |
● Full turnkey (All components sourced by Yingstar); ● Partial turnkey; ● Kitted/Consigned |
||||
| Solder Types | Leaded; Lead-Free(Rohs);Water soluble solder paste | ||||
| Order quantity |
● 5pcs to 100,000pcs; ● From Prototypes to Mass Production |
||||
| Assembly Lead Time | From 8 hours to 72 hours when parts are ready | ||||