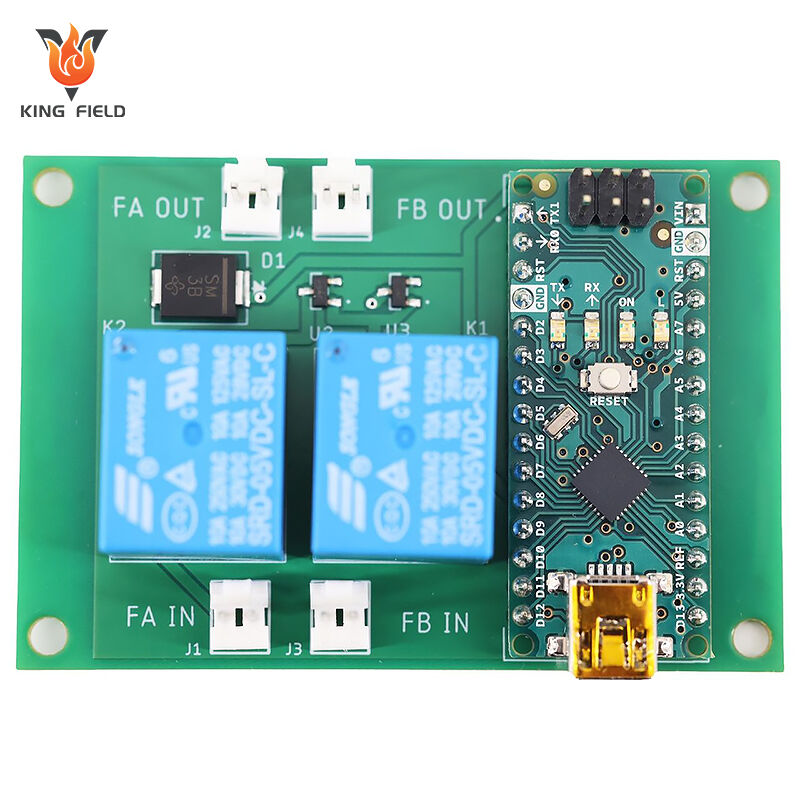
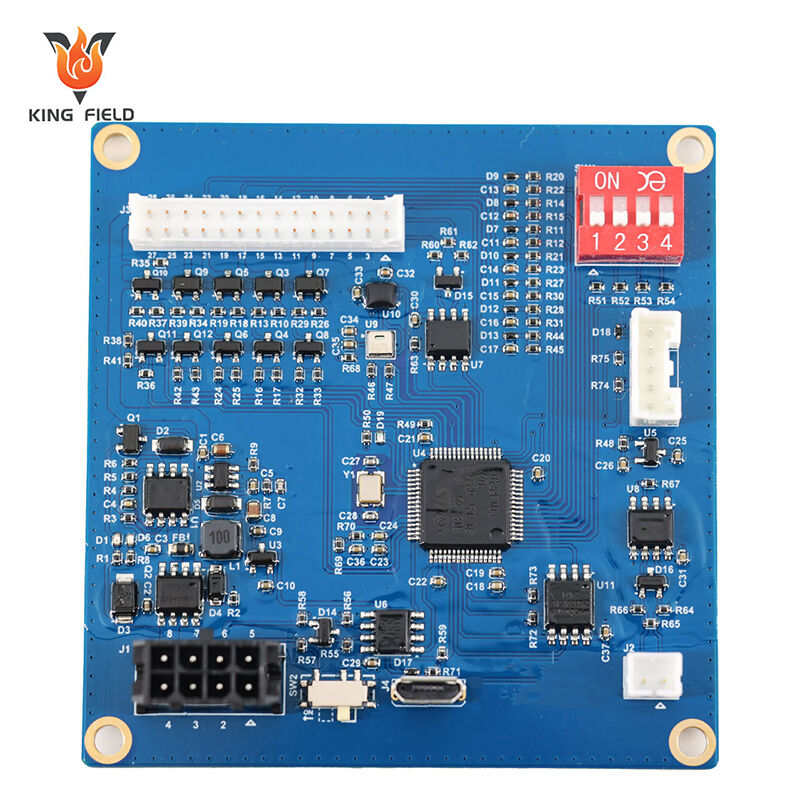
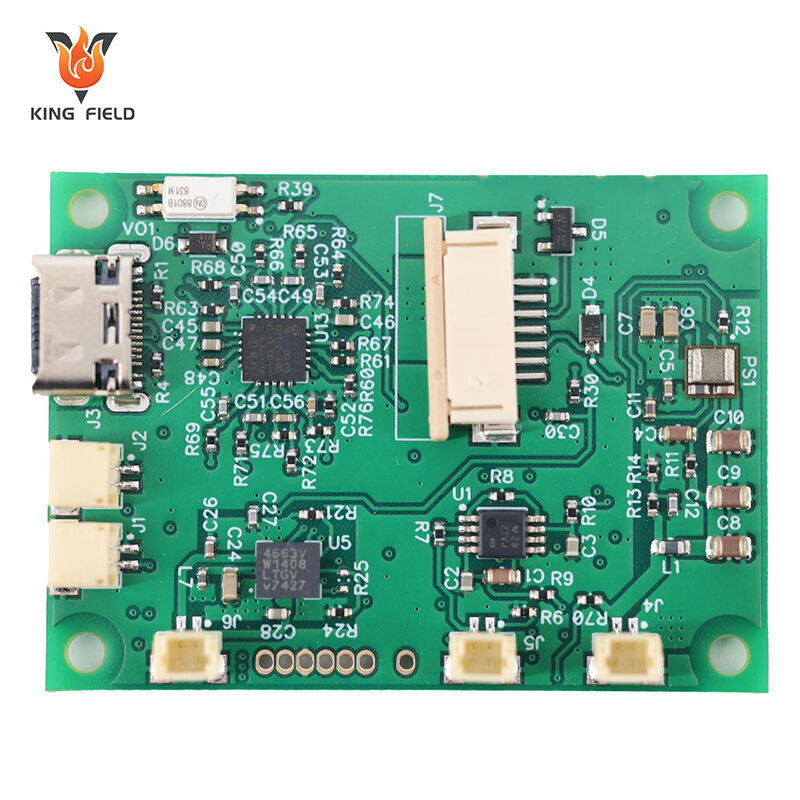
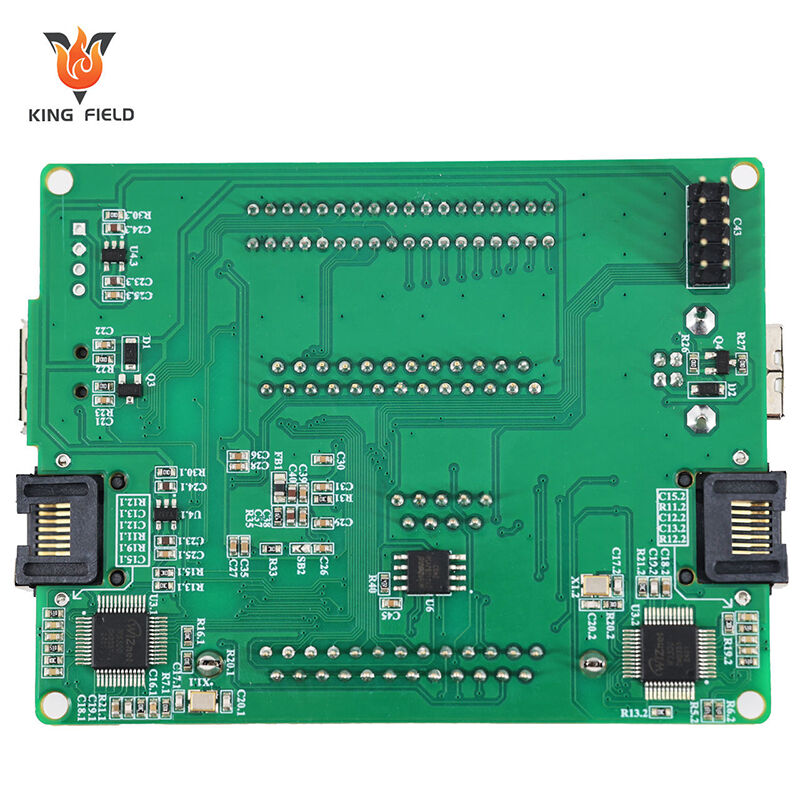
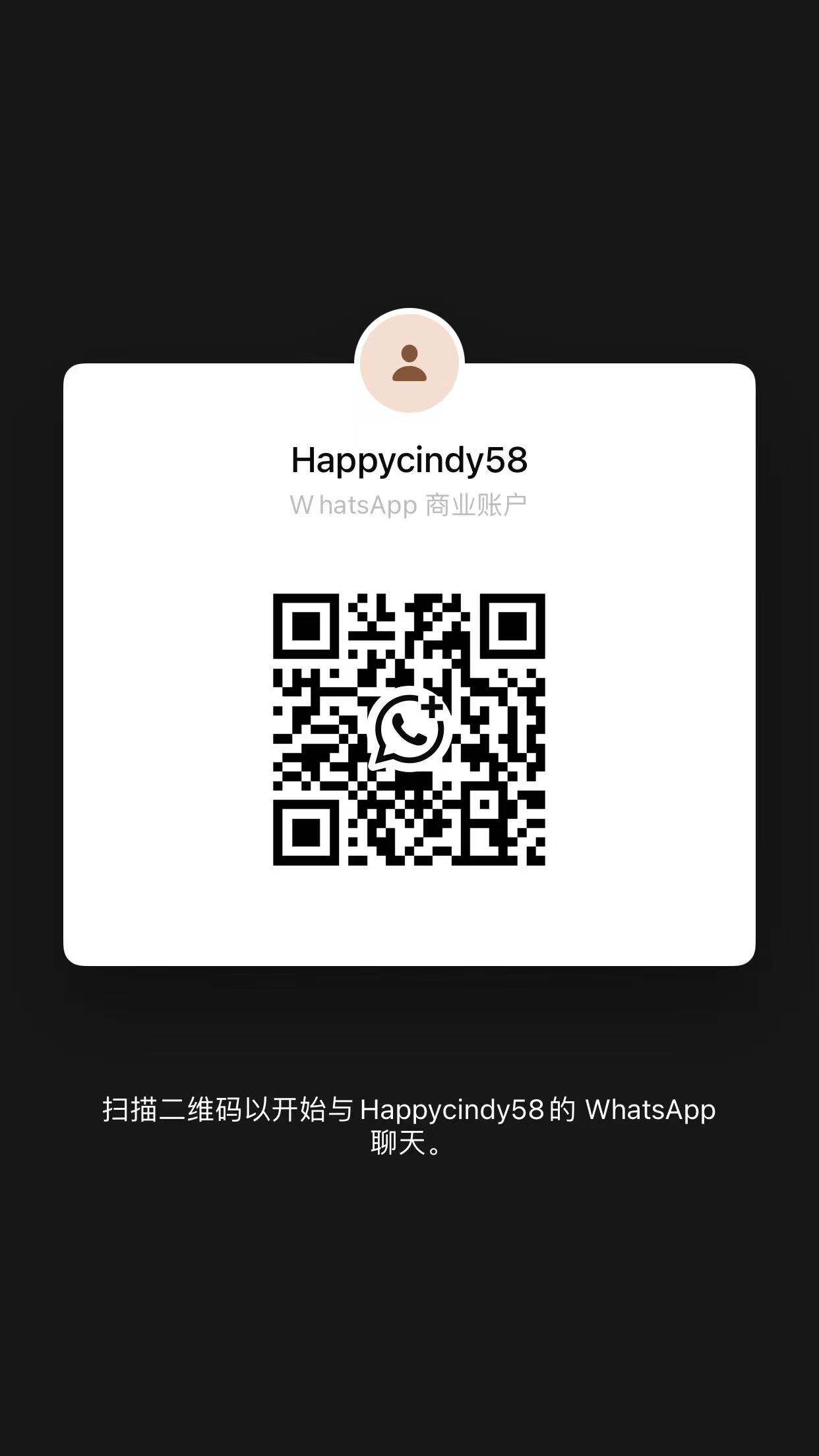
Through-Hole Assembly
Reliable Through Hole Assembly for medical/industrial/automotive/consumer electronics—specialized in robust, high-power component integration. Ideal for devices requiring durable solder joints, heavy-duty connectors, and stable power transmission.
IPC-A-610 compliant, with precision soldering (wave/solder paste), strict quality testing (AOI/ICT), and seamless compatibility with mixed assembly workflows. 24h prototyping, scalable mass production, and DFM support ensure cost-effective, long-lasting solutions for industrial control systems, power modules, and ruggedized devices.
Description
What is Through-Hole PCB Assembly?
Through Hole PCB Assembly is a traditional electronic manufacturing process where components with metal leads are inserted through pre-drilled holes in a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) and soldered to the opposite side. Unlike Surface Mount Technology (SMT), THT components are physically anchored through the PCB, making them ideal for applications requiring mechanical stability and high-power handling.
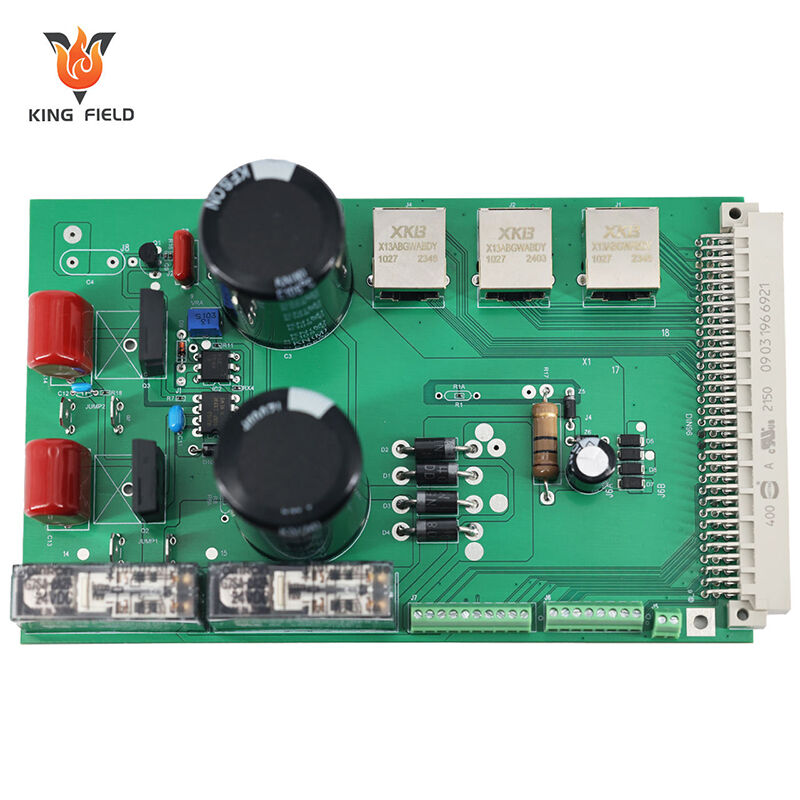

Core Characteristics of THT Assembly
· Component Design: THT components have long, rigid leads that pass through PCB holes, creating a strong mechanical bond.
· Soldering Methods:
Wave Soldering: Automated process for high-volume production – PCBs are passed over a wave of molten solder to bond all leads simultaneously.
Manual Soldering: Used for low-volume production, prototype assembly, or large/odd-shaped components that cannot be wave-soldered.
· Mechanical Strength: The through-hole insertion and soldering create a robust connection, resistant to vibration, shock, and physical stress.
· Power Handling: THT components are optimized for high-current, high-voltage applications due to their larger lead size and stronger thermal dissipation.
Key THT Assembly Process Steps
· Component Preparation: Trim component leads to the correct length (if needed) for PCB insertion.
· Insertion: Place component leads through pre-drilled PCB holes (manual for prototypes, automated with insertion machines for mass production).
Soldering:
Wave soldering: PCB (with inserted components) is conveyed over a solder wave, which coats the exposed leads and pads to form a permanent bond.
Manual soldering: Use a soldering iron to apply solder to individual leads for precise, custom connections.
· Trimming & Cleaning: Cut excess lead length after soldering; clean the PCB to remove flux residues (critical for reliability and compliance).
· Inspection & Testing: Visual inspection (or automated X-ray for hidden joints) to check for cold solder joints, bridges, or misaligned components; functional testing to validate performance.
Advantages of THT Assembly
· Superior Mechanical Stability: Ideal for applications subject to vibration or frequent mating/unmating.
· High-Power/High-Voltage Compatibility: Handles higher current and voltage than most SMDs, making it essential for power supplies, industrial control panels, and automotive battery systems.
· Ease of Repair & Rework: Damaged components can be easily removed and replaced (no need for specialized reflow equipment), reducing downtime for critical systems.
· Reliability in Harsh Environments: Resistant to extreme temperatures, moisture, and chemical exposure (compliant with standards like IEC 60335 for industrial use, IATF 16949 for automotive).
Industry-Specific Applications
| Industry | THT Assembly Use Cases | ||||
| Medical | Power supply units for diagnostic equipment (MRI/CT scanners), surgical tool connectors – meets ISO 13485 for safety and durability. | ||||
| Industrial Control | Motor controllers, PLC power modules, high-voltage terminal blocks – compliant with UL 508 and IEC 60335 for industrial safety. | ||||
| Automotive | Battery terminals, engine control unit (ECU) power connectors, lighting system components – withstands vibration and temperature extremes (IATF 16949). | ||||
| Consumer Electronics | Power cord connectors for home appliances (refrigerators, washing machines), audio equipment jacks – durable for frequent use. | ||||
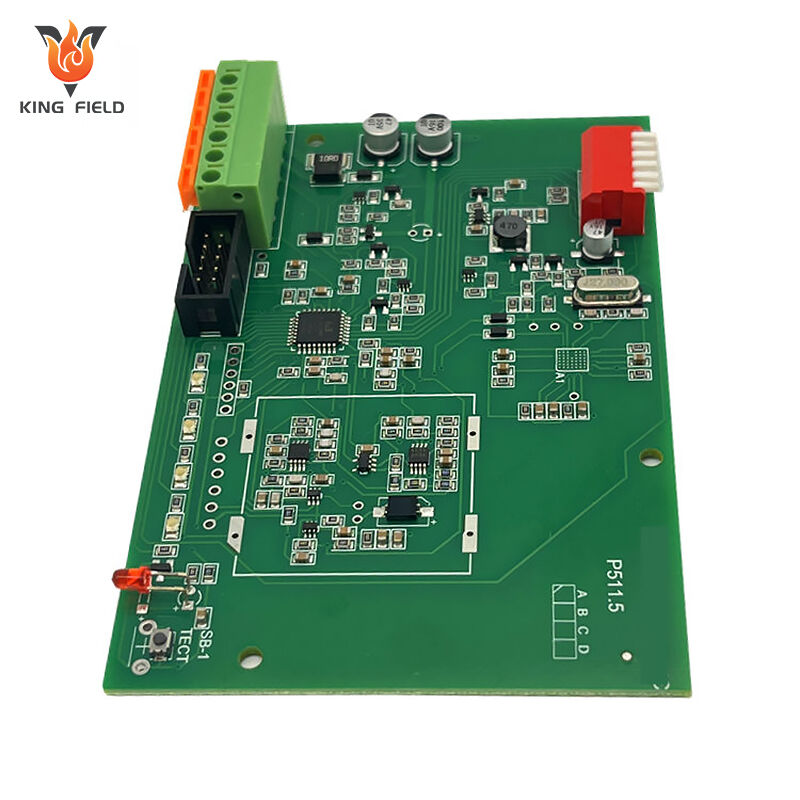
THT vs. SMT: Key Differentiators
| Aspect | THT Assembly | SMT Assembly | |||
| Mechanical Strength | High (resistant to vibration/shock) | Low (best for stable environments) | |||
| Power Handling | High (high-current/voltage) | Low (low-to-medium power) | |||
| Component Size | Larger | Smaller (miniaturized) | |||
| Production Speed | Slower (semi-automated/manual) | Faster (fully automated) | |||
| Space Efficiency | Lower (requires PCB holes) | Higher (surface-mounted, no holes) | |||
Why Choose Through Hole PCB Assembly?
Why Choose Through Hole PCB Assembly?
Choosing Through Hole PCB Assembly (THT) is strategic for applications where mechanical robustness, high-power handling, and long-term reliability are non-negotiable—especially across medical, industrial control, automotive, and consumer electronics sectors. Below are the core reasons to select THT, tailored to your business focus:
Unmatched Mechanical Durability for High-Stress Environments
THT components are physically anchored through PCB holes and soldered on the opposite side, creating a far stronger bond than surface-mounted devices (SMDs). This makes THT ideal for:
· Vibration/shock-prone applications: Automotive chassis components, industrial robotics, and outdoor equipment (compliant with IATF 16949 and IEC 60335 standards).
· Frequent mating/unmating: Power connectors, audio jacks, and industrial terminal blocks (resistant to wear from repeated use).
· Harsh operating conditions: Extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemical exposure.
Superior High-Power/High-Voltage Performance
THT components are engineered to handle higher current, voltage, and thermal loads than most SMDs, critical for:
· Power systems: Industrial power supplies, medical device power units (MRI/CT scanners), and automotive battery terminals.
· High-voltage equipment: Industrial control panels, HVAC systems, and electric vehicle (EV) charging components.
· Thermal management: Larger component size and direct PCB mounting enable better heat dissipation, reducing failure risk in continuous-operation systems.
Ease of Repair, Rework, and Maintenance
THT’s design simplifies post-production servicing—a key advantage for mission-critical equipment:
· Cost-effective repairs: Damaged components can be quickly replaced without specialized reflow equipment, minimizing downtime.
· Prototype flexibility: Ideal for low-volume prototyping or custom builds, where manual adjustments and component swaps are common.
· Long lifecycle support: THT components are often more readily available for legacy systems, ensuring ongoing maintainability.

Compliance with Industry-Specific Safety Standards
THT aligns with strict regulatory requirements for safety and reliability:
· Medical: Meets ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820 for critical power connections in diagnostic equipment and surgical tools.
· Industrial Control: Complies with UL 508 and IEC 60335 for high-voltage terminal blocks and motor controllers.
· Automotive: Adheres to IATF 16949 for vibration-resistant components and safety-critical systems.
Compatibility with Mixed Assembly (THT + SMT)
THT complements SMT to solve complex design challenges:
· Use THT for high-power/durable components and SMT for miniaturized circuitry on the same PCB.
· Balance cost and performance: THT handles custom, low-volume high-power parts while SMT automates mass production of standard components.
Reliability for Safety-Critical Applications
THT’s robust connections reduce failure risk in systems where downtime or malfunctions have severe consequences:
· Medical devices: Power connections for patient monitors and life-support equipment.
· Industrial automation: Emergency stop systems and robotic control modules.
· Automotive: Brake system sensors and battery management system (BMS) terminals.
Features of Through Hole PCB Assembly
Through Hole PCB Assembly (THT) is defined by distinct features that make it irreplaceable for applications requiring mechanical robustness, high-power handling, and long-term reliability. Below is a structured breakdown of its core features, aligned with medical, industrial control, automotive, and consumer electronics sectors:
Mechanical Strength & Durability
Anchored Connection Design: Components are inserted through PCB holes and soldered on the opposite side, creating a rigid mechanical bond (far stronger than surface-mounted components). This resists vibration, shock, and physical stress—critical for:
Automotive chassis components (IATF 16949 compliance for vibration resistance).
Industrial robotics and outdoor equipment (resistance to frequent movement/impact).
Medical device connectors (durability for repeated sterilization cycles).
Resistance to Wear: Through-hole connectors and terminals withstand frequent mating/unmating.
High-Power & High-Voltage Capability
Robust Current/Voltage Handling: Larger component leads and solder joints enable THT to support high-current (10A+) and high-voltage (1000V+) applications, unlike most SMDs:
Industrial power supplies and motor controllers (high-power transformers/resistors).
Automotive EV battery systems (high-voltage terminals and fuses).
Medical MRI/CT scanners (high-voltage power conversion components).
Superior Thermal Dissipation: Larger component size and direct PCB mounting facilitate heat transfer, reducing overheating risk in continuous-operation systems.
Ease of Manual Assembly, Repair & Rework
· Accessible Soldering: THT components are visible and easy to solder manually—ideal for low-volume prototyping, custom builds, or field repairs.
· Simplified Component Replacement: Damaged components can be removed and replaced without specialized reflow equipment, minimizing downtime for critical systems.
· Legacy System Compatibility: THT components are widely available for older equipment, ensuring long-term maintainability.
Reliability in Harsh Environments
· Environmental Resistance: THT assemblies perform consistently in extreme conditions:
Temperature extremes (-40°C to 150°C) for automotive underhood systems.
Moisture/dust (IP65/IP67 ratings) for outdoor industrial sensors.
Chemical exposure (oils, solvents) for factory floor equipment.
· Stable Electrical Performance: Less susceptible to EMI/RFI interference in noisy industrial environments.
Compliance with Strict Industry Standards
· Safety-Critical Certification: THT aligns with regulatory requirements for reliability and safety:
Medical: ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
Industrial: UL 508 and IEC 60335.
Automotive: IATF 16949.
· Traceability: Through-hole components are easier to inspect and validate for compliance.
Compatibility with Mixed Assembly (THT + SMT)
· Hybrid Design Flexibility: THT integrates seamlessly with SMT on the same PCB, combining:
THT for high-power/durable components.
SMT for miniaturized circuitry.
· Cost Optimization: Balances the low-volume customizability of THT with the mass-production efficiency of SMT.
Simple Inspection & Quality Control
· Visual Verifiability: Solder joints are visible (unlike hidden SMD joints), enabling quick visual inspection or automated optical inspection (AOI) for defects (cold solder joints, bridges).
· Test Accessibility: Through-hole leads are easy to probe for functional testing.
Production Capacity
| Assembly Types |
● SMT Assembly( with AOI inspection); ● BGA Assembly(with X-Ray inspection); ● Through-hole Assembly; ● SMT & Through-hole Mixed Assembly; ● Kit Assembly |
||||
| Quality Inspection |
● AOI Inspection; ● X-Ray Inspection; ● Voltage Test; ● Chip Programming; ● ICT Test; Functional Test |
||||
| PCB Types | Rigid PCB、Metal core PCB、Flex PCB、Rigid-Flex PCB | ||||
| Component Types |
● Passives, smallest size 0201(inch) ● Fine-pitch chips to 0.38mm ● BGA (0.2mm pitch), FPGA, LGA, DFN,QFN with X-Ray testing ● Connectors and terminals |
||||
| Components Sourcing |
● Full turnkey (All components sourced by Yingstar); ● Partial turnkey; ● Kitted/Consigned |
||||
| Solder Types | Leaded; Lead-Free(Rohs);Water soluble solder paste | ||||
| Order quantity |
● 5pcs to 100,000pcs; ● From Prototypes to Mass Production |
||||
| Assembly Lead Time | From 8 hours to 72 hours when parts are ready | ||||