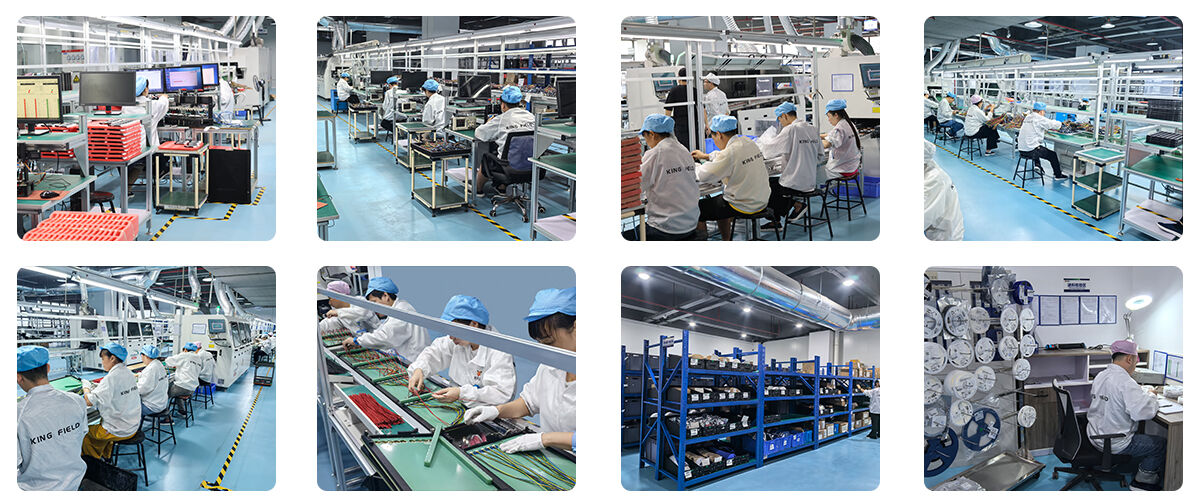
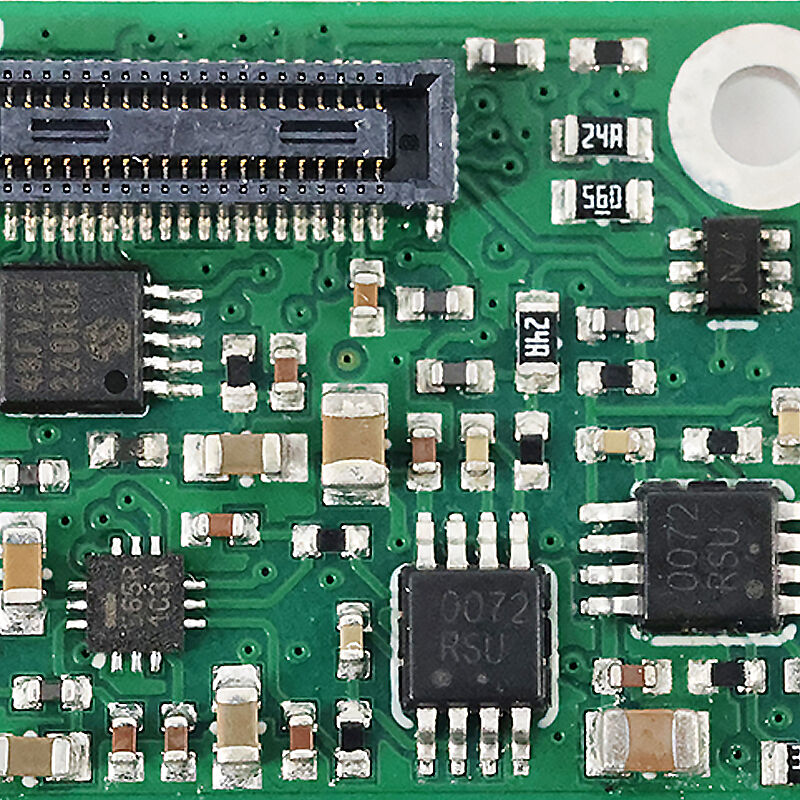
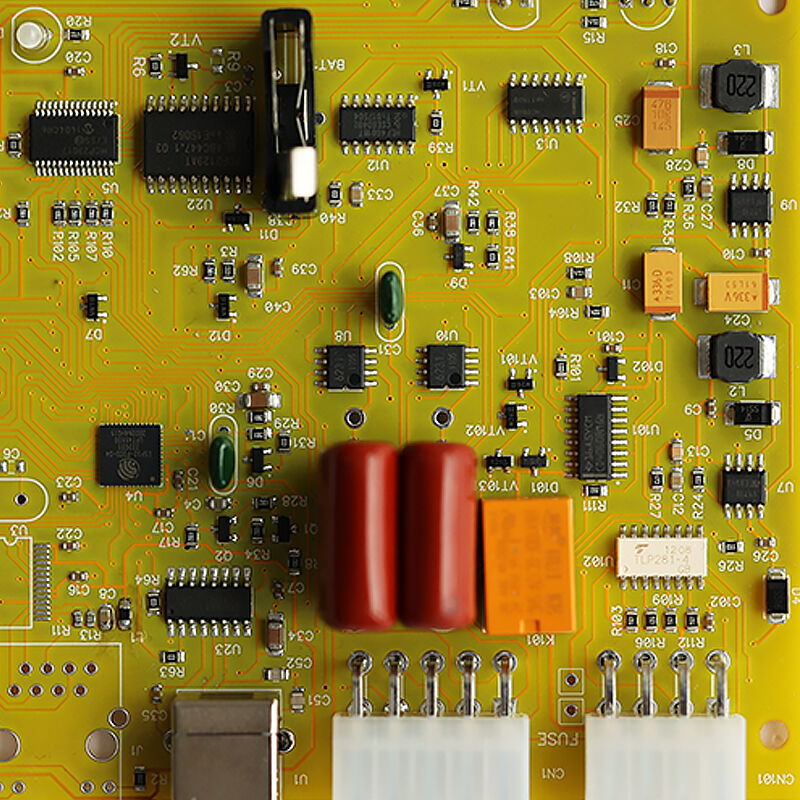
Mixed Assembly Advantages
Kingfield’s Mixed Assembly (SMT + Through-Hole) delivers versatile, reliable solutions for medical/industrial/automotive/consumer electronics. Seamlessly combines surface-mount precision and through-hole durability—ideal for complex devices needing both fine-pitch components and robust power connections.
✅ SMT+Through-Hole integration
✅ IPC-A-610 compliant + AOI/ICT quality validation
✅ One-stop turnkey assembly
Description
Mixed Assembly Advantages
Mixed assembly (combining Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT)) leverages the strengths of both methods to address the limitations of single-technology assembly, making it ideal for complex electronic products across medical, industrial control, automotive, and consumer electronics sectors. Below are its core advantages:

Optimized Component Selection & Functional Performance
SMT for miniaturization/density: SMDs handle high-density, compact components critical for space-constrained devices.
THT for durability/mechanical strength:
Through-hole components provide superior mechanical stability for high-stress applications or components requiring frequent mating/unmating.
Balanced electrical performance: SMT minimizes signal delay (ideal for high-frequency circuits), while THT supports high-power, high-current applications where robust connections are essential.
Enhanced Reliability for Diverse Operating Environments
Harsh environment resilience:
THT components resist vibration, shock, and temperature extremes (critical for automotive underhood systems, industrial robotics), while SMT ensures compact, reliable circuitry for sensitive electronics.
Redundancy for critical systems: Mixed assembly reduces single-point failures – e.g., medical devices use SMT for precision sensors and THT for power connectors to ensure both accuracy and safety.
Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Flexibility for low-to-high volume: SMT automates mass production of small components, while THT handles low-volume, custom high-power components (avoiding the cost of custom SMD power parts).
Reduced rework costs: THT simplifies repair/replacement of large, expensive components, while SMT ensures efficient production of standard circuitry – balancing upfront and lifecycle costs.
Leverages existing infrastructure: Manufacturers can use existing SMT/THT equipment instead of investing in specialized single-technology lines, lowering capital expenditure.

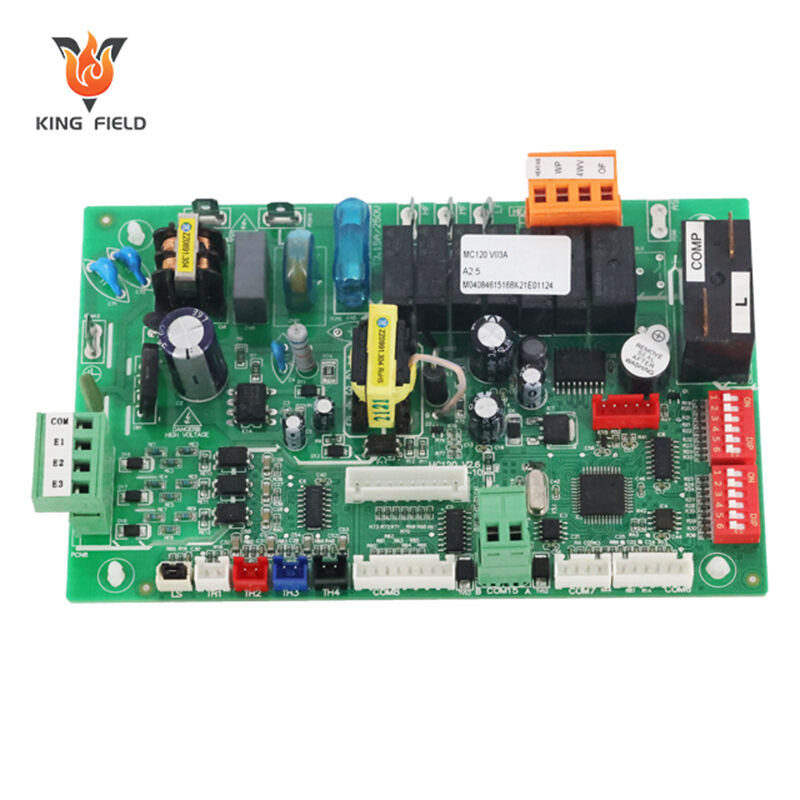
Compliance with Industry-Specific Requirements
| Industry | Mixed Assembly Compliance Benefits | ||||
| Medical | SMT meets miniaturization needs for wearable devices; THT ensures compliance with ISO 13485 for high-power medical equipment. | ||||
| Industrial Control | THT supports IEC 60335 safety standards for high-voltage components; SMT enables compact PLC designs with high-density I/O modules. | ||||
| Automotive | THT components comply with IATF 16949 for vibration resistance; SMT delivers miniaturized ADAS circuitry. | ||||
| Consumer Electronics | SMT reduces device size; THT provides durable USB/HDMI connectors for frequent use. | ||||
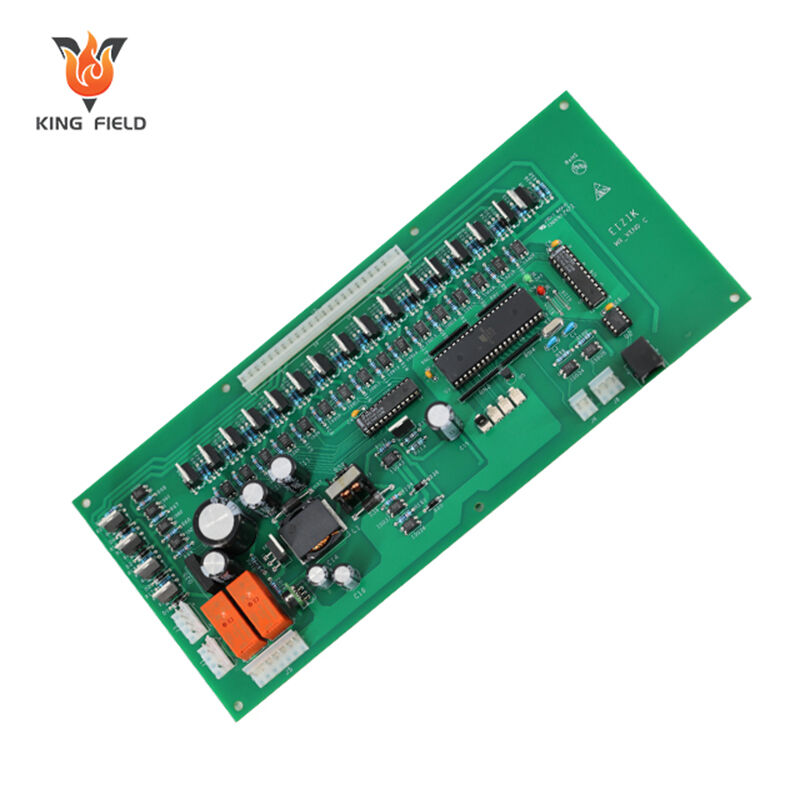
Design Flexibility for Complex Products
Hybrid circuit design: Enables integration of both high-density signal circuits (SMT) and high-power circuits (THT) on a single PCB.
Adaptability to custom requirements: Supports unique product needs.
Benefit
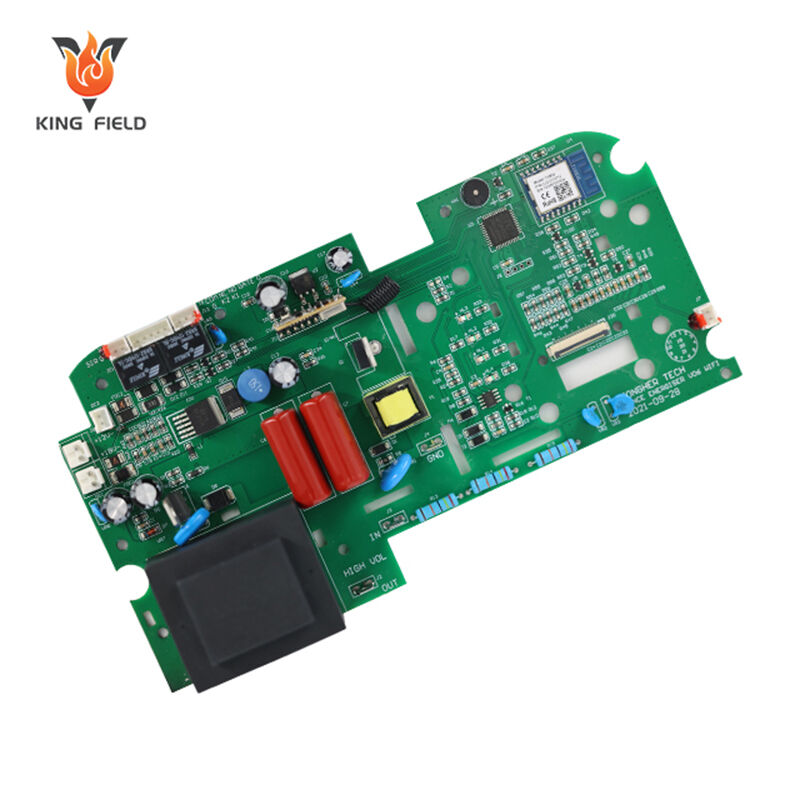
Performance and Function Optimization: Balancing Precision and Durability
Complementary Technical Characteristics:
SMT handles high-density, miniaturized components, meeting the space constraints of medical wearable devices and automotive ECUs;
THT handles high-mechanical-strength, high-power components, adapting to the durability requirements of frequent plugging and unplugging in industrial control equipment and the vibration environment of automotive chassis.
Balanced Electrical Performance:
SMT shortens signal paths and reduces EMI interference, ensuring the high-frequency signal stability of medical diagnostic equipment and consumer electronics IoT modules;
THT supports high-current transmission, meeting the high-power requirements of industrial control power supplies and automotive power battery interfaces.
Improved Reliability: Adapting to Complex Application Environments
Harsh Environment Tolerance:
THT components have strong vibration and shock resistance (compliant with IATF 16949 automotive standards), suitable for automotive engine compartments, industrial robots, and other scenarios;
SMT ensures a low failure rate for precision circuits in stable environments.
Redundancy Protection for Critical Systems:
In medical devices, SMT handles the core detection module, and THT handles the power connection part. This dual technology path reduces the risk of single-point failure and complies with ISO 13485 safety requirements.
Cost and Production Efficiency Optimization
Flexible Adaptation to Production Scale:
SMT automated production lines meet the large-scale production needs of consumer electronics and automotive components, reducing unit costs;
THT supports small-batch customization of high-power components for industrial control and medical applications, avoiding the high costs of customized SMD high-power devices.
Reduced Total Cost of Ownership:
THT components are easy to repair and replace, reducing equipment downtime; SMT components have high production efficiency, balancing initial production and subsequent maintenance costs.
Reuse of Existing Production Lines: No need to purchase separate SMT/THT dedicated equipment, reducing capital investment in production line upgrades.
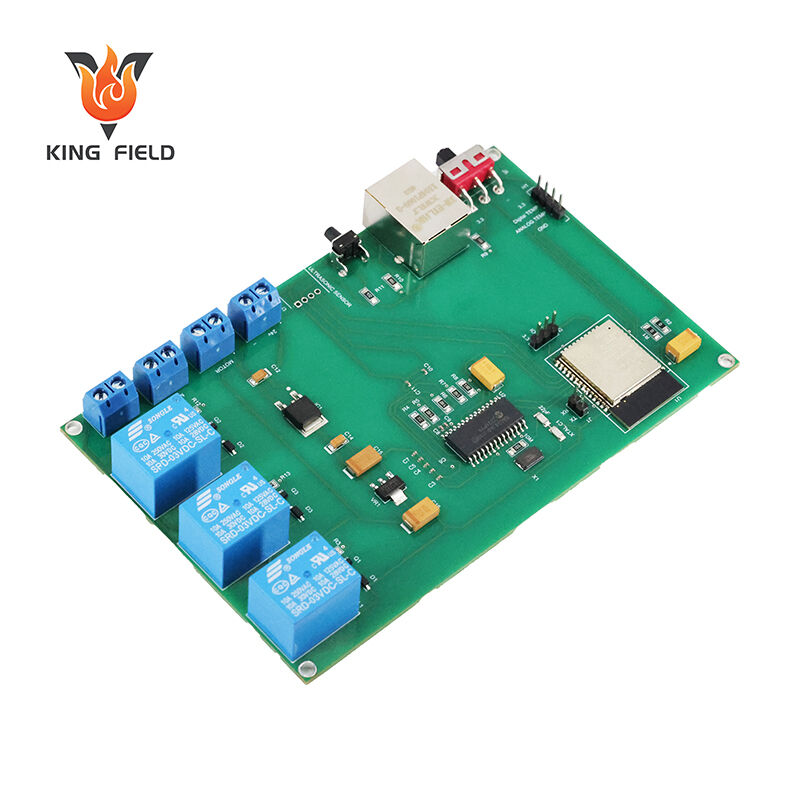
Industry compliance and customized adaptation
| Industries: | Compliance and Customization Value of Mixed Assembly | ||||
| Medical | SMT meets the miniaturization requirements of wearable devices, while THT adapts to the ISO 13485 compliance standards for high-power medical equipment. | ||||
| Industrial Control | THT components comply with IEC 60335 high-voltage safety standards, and SMT enables high-density I/O module design for PLCs, balancing safety and integration. | ||||
| Automotive | THT connectors meet IATF 16949 vibration resistance requirements, and SMT supports miniaturized circuits for ADAS systems, adapting to automotive space constraints. | ||||
| Consumer Electronics | SMT reduces the size of smart devices, while THT provides durable USB/HDMI interfaces, suitable for high-frequency plugging and unplugging scenarios. | ||||
Design Flexibility: Supports Complex Product Development
A single PCB can integrate SMT high-frequency signal circuits and THT high-power circuits;
Adapts to customized needs, eliminating the need to split product designs.
Manufacturing Parameters
| Equipment manufacturing process capability | |||||
| SMT Capacity | 60,000,000 chips/day | ||||
| THT Capacity | 1.500,000 chips/day | ||||
| Delivery Time | Expedited 24 hours | ||||
| Types of PCBs Available for Assembly | Rigid boards, flexible boards, rigid-flex boards, aluminum boards | ||||
| PCB Specifications for Assembly | Maximum size: 480x510 mm; Minimum size: 50x100 mm | ||||
| Minimum Assembly Component | 01005 | ||||
| Minimum BGA | Rigid boards 0.3 mm; Flexible boards 0.4 mm | ||||
| Minimum Fine-Pitch Component | 0.2 mm | ||||
| Component Placement Accuracy | ±0.015 mm | ||||
| Maximum Component Height | 25 mm | ||||
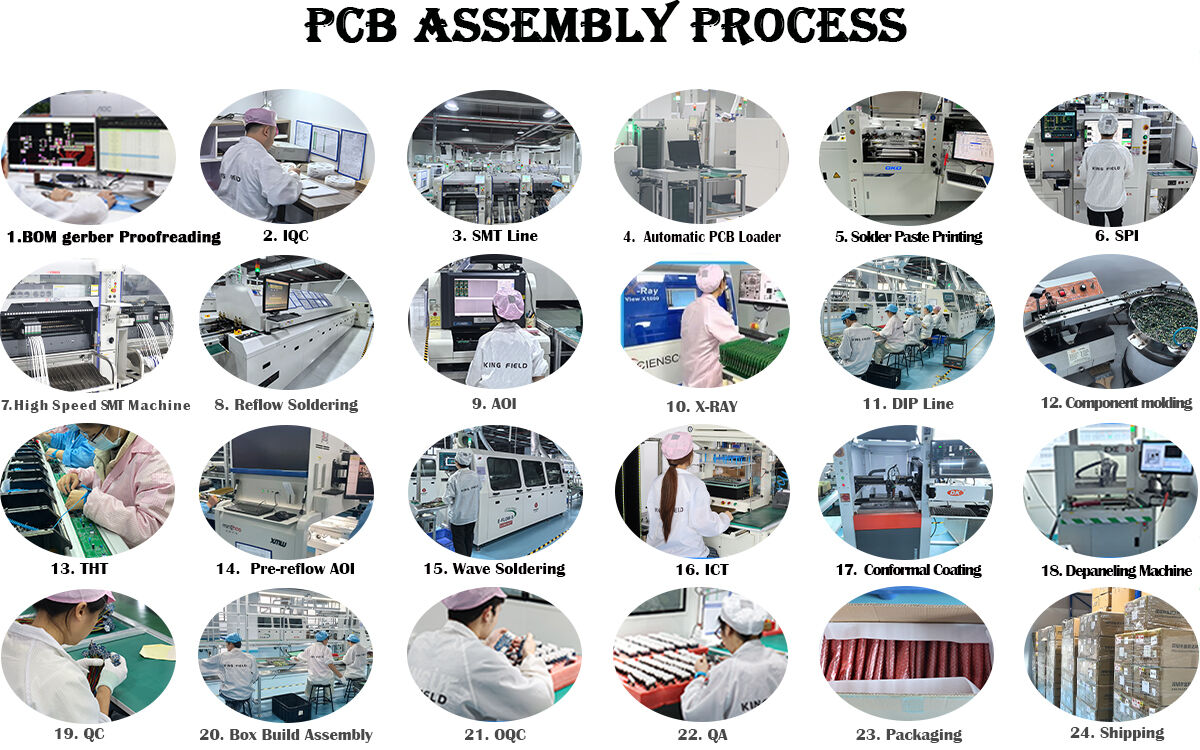
Production Capacity
| Assembly Types |
● SMT Assembly( with AOI inspection); ● BGA Assembly(with X-Ray inspection); ● Through-hole Assembly; ● SMT & Through-hole Mixed Assembly; ● Kit Assembly |
||||
| Quality Inspection |
● AOI Inspection; ● X-Ray Inspection; ● Voltage Test; ● Chip Programming; ● ICT Test; Functional Test |
||||
| PCB Types | Rigid PCB、Metal core PCB、Flex PCB、Rigid-Flex PCB | ||||
| Component Types |
● Passives, smallest size 0201(inch) ● Fine-pitch chips to 0.38mm ● BGA (0.2mm pitch), FPGA, LGA, DFN,QFN with X-Ray testing ● Connectors and terminals |
||||
| Components Sourcing |
● Full turnkey (All components sourced by Yingstar); ● Partial turnkey; ● Kitted/Consigned |
||||
| Solder Types | Leaded; Lead-Free(Rohs);Water soluble solder paste | ||||
| Order quantity |
● 5pcs to 100,000pcs; ● From Prototypes to Mass Production |
||||
| Assembly Lead Time | From 8 hours to 72 hours when parts are ready | ||||