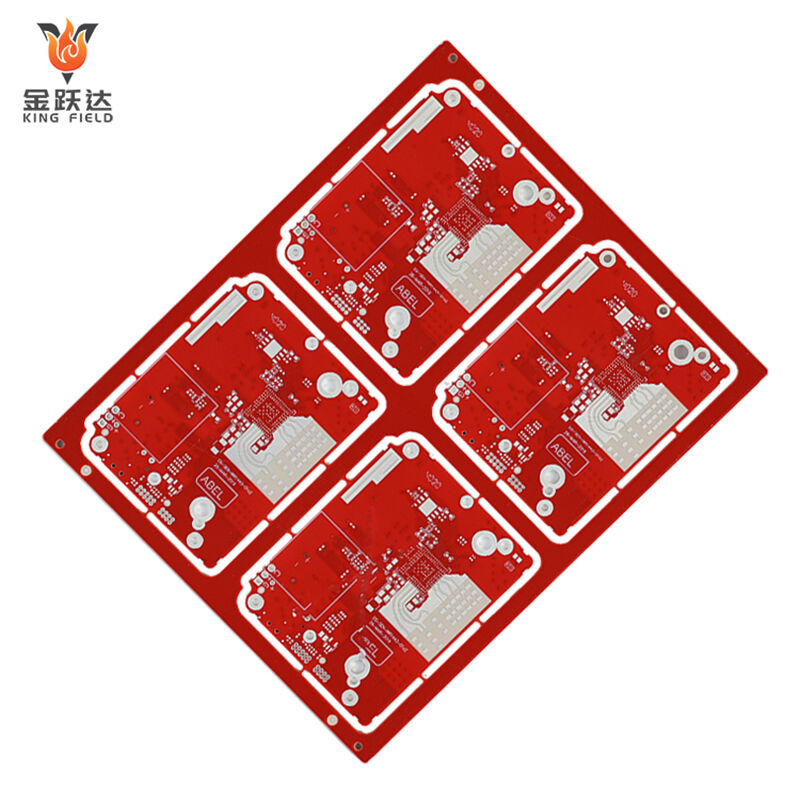
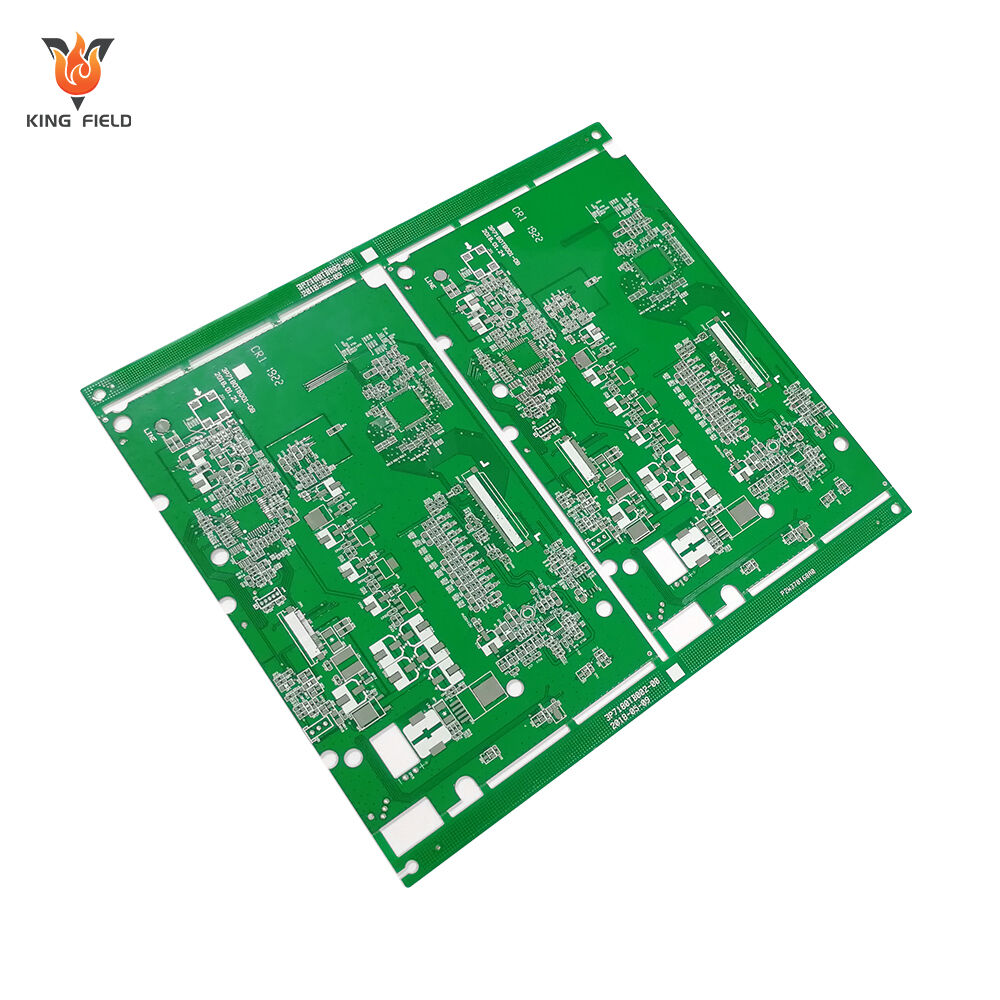
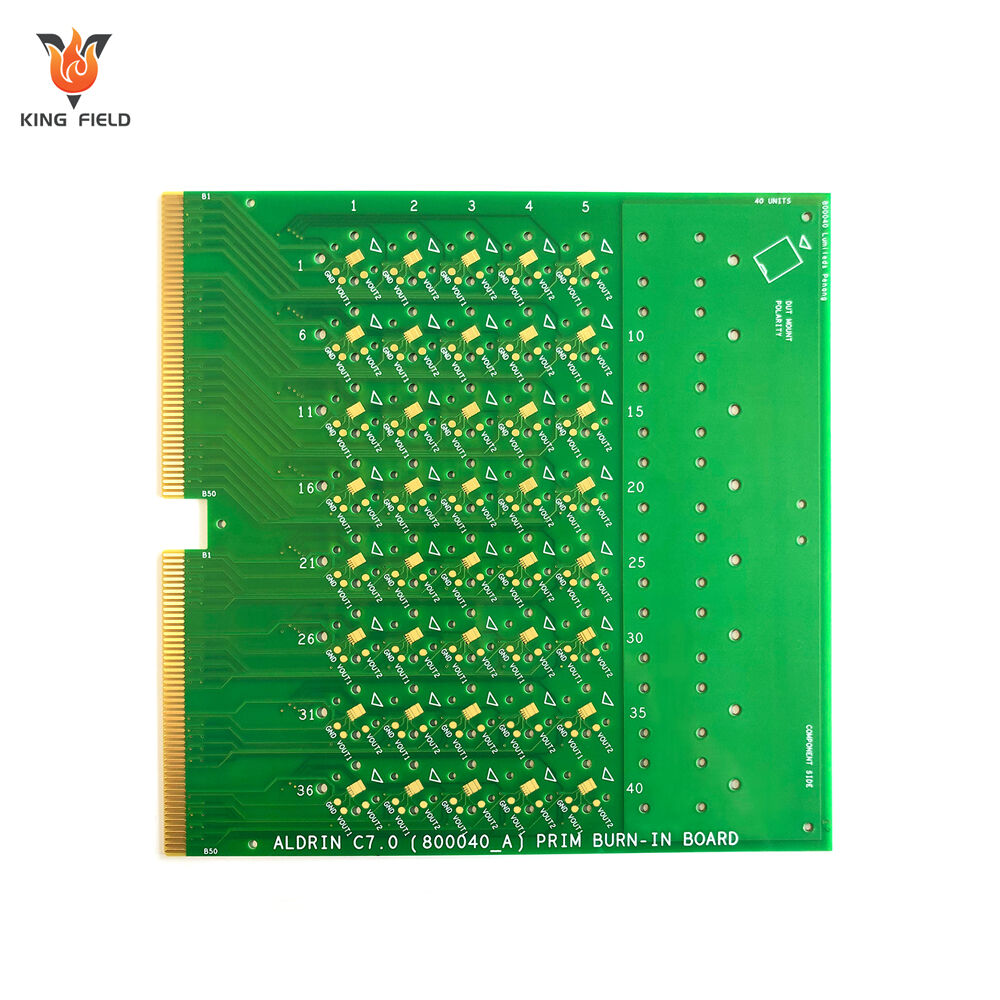
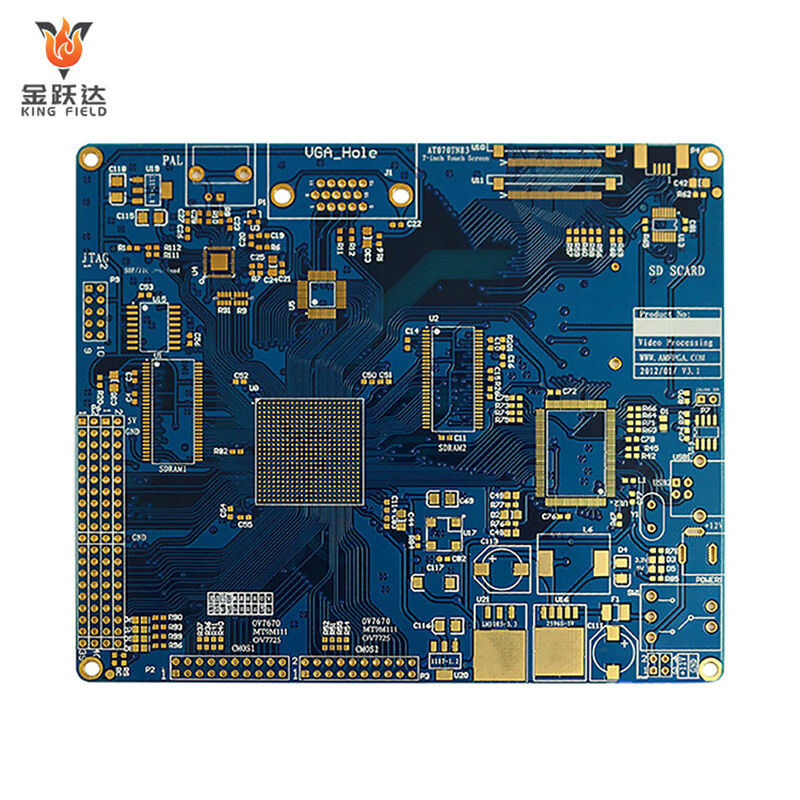
Standard PCB
Reliable Standard PCBs for industrial/automotive/consumer/medical electronics. Cost-effective, durable FR4-based design with precise circuitry—paired with 24h prototyping, fast delivery, DFM support & AOI testing.
✅ FR4 substrate
✅ Multi-industry universal compatibility
✅ Quality validation for consistent performance
Description
The meaning of Standard PCBs
Standard PCBs generally refer to printed circuit boards manufactured based on industry-standard specifications, using mature processes and conventional substrates. They are a concept relative to specialty PCBs . Their core characteristics are high versatility, standardized processes, and controllable costs. They primarily meet the basic circuit connection needs of common scenarios such as consumer electronics and industrial control.
Substrate Standardization
The mainstream uses FR-4 epoxy resin fiberglass board (accounting for more than 90% of the total standard PCBs), while phenolic paperboard (FR-1/FR-2) is used in a few applications. The substrate performance meets the general standards of IPC, UL and other standards. For example, FR-4 has a glass transition temperature (Tg) of about 130~150℃, thermal conductivity of 0.3~0.5 W/(m・K) and dielectric constant (Dk) of 4.2~4.7@1GHz. It has stable performance and low cost.
Process standardization
Following globally accepted PCB manufacturing processes (material preparation → drilling → copper plating → electroplating → exposure → etching → solder mask → surface treatment → molding → testing), processing parameters and precision requirements are all standardized within the industry:
· Standard line width/spacing: ≥0.1mm (4mil);
· Minimum hole diameter: ≥0.3mm;
· Surface treatment: Prefers standardized processes such as HASL (High-Speed Iron Lamination), ENIG (Engineering Injection Gold), and nickel-gold plating;
· Number of layers: Primarily single/double-sided boards, multi-layer boards (4~8 layers) are also within the standard range (more than 12 layers are mostly classified as high-end PCBs).

The core difference between standard PCBs and special PCBs
| Standard PCB | Specialty PCBs | ||||
| substrate | FR-4 epoxy resin fiberglass board, phenolic paperboard | Ceramics, PTFE composites, polyimide (PI), etc. | |||
| Process characteristics | Fully standardized, with a high mass production yield (≥98%). | Customized processes, some of which require specialized equipment . | |||
| Performance focus | Basic circuit connection, no special performance requirements. | Meeting special requirements such as heat dissipation, high frequency, flexibility, and high temperature resistance | |||
| cost | Low cost (FR-4 substrate costs only 1/10 of ceramic PCBs) | High (the cost of substrate and manufacturing process is 5 to 50 times that of standard PCBs) | |||
| Applicable Scenarios | Standard circuit connection (low power, low frequency, normal temperature environment) | High-frequency communication, high-power heat dissipation, extreme environments, and irregular structures | |||
Common types
Classified by number of layers:
· Single-sided PCB: Only one side has circuitry, lowest cost, suitable for simple circuits;
· Double-sided PCB: Both sides have circuitry, interconnected via vias, the mainstream type of standard PCB;
· Multilayer PCB (4-8 layers): Includes inner layer circuitry, suitable for complex circuits , still within the standard category.
· Classified by structure: All are rigid PCBs (flexible PCBs are special PCBs), with fixed shape and cannot be bent.
Advantages
Standard PCBs (primarily based on FR-4 substrate) have become the most widely used type of circuit board in electronic devices due to their core characteristics of standardization, versatility, and high cost-effectiveness. Their specific advantages are as follows:
Ultimate cost advantage
· Low substrate cost: FR-4 epoxy resin fiberglass board is currently the PCB substrate with the largest mass production scale. The raw material price is only 1/10 to 1/50 of that of special substrates such as ceramic and Rogers, and the supply is stable;
· Low process cost: It adopts a fully standardized manufacturing process, without the need for special equipment or customized processes, and the mass production yield is as high as 98% or more, further reducing the unit cost;
· Low procurement cost: The market supply is sufficient, and the upstream and downstream industrial chains are mature (board, processing, testing).
Low unit price can be obtained even for small and medium batch purchases, making it suitable for cost-sensitive products such as consumer electronics and small home appliances.
Mature standardization system
· Design standardization: Following globally recognized standards such as IPC-2221 and UL, designers can directly use mature design libraries without re-verification;
· Process standardization: From drilling and electroplating to solder masking and molding, all processes have clear industry standards, and standard PCBs produced by different manufacturers are highly compatible, so there is no need to adjust the design when changing suppliers;
· Testing standardization: Verification processes such as continuity testing, insulation testing, and solderability testing are unified, and product quality can be quantified and traced, reducing quality risks.
Wide range of versatility and adaptability
· Scenario Adaptability:
Covers over 90% of conventional electronic devices, including consumer electronics (TVs, routers), industrial control (ordinary PLCs), office equipment (printers), and automotive electronics (in-vehicle entertainment systems), eliminating the need for customization for single scenarios.
· Component Compatibility:
Supports all conventionally packaged components , adapting to mainstream soldering processes such as THT and SMT, offering high design flexibility.
· Layer Coverage:
From single-sided boards to 8-layer boards, all fall within the standard PCB category, meeting the needs of everything from simple circuits to complex circuits.
Stable basic performance
· Reliable electrical performance: Stable dielectric constant , insulation strength meets the requirements of conventional low-voltage/high-voltage circuits, and signal transmission loss is negligible in low-frequency (<2GHz) scenarios;
· Meets mechanical performance standards: High hardness and not easily deformed, the 1.6mm thick FR-4 PCB can withstand conventional installation stress, meeting the structural support requirements of the equipment;
· Environmental adaptability: Long-term performance does not degrade in normal temperature (-20℃~85℃) and dry environment, suitable for the use conditions of most indoor electronic equipment.
Convenient supply chain and delivery
· Short production cycle: Standardized processes eliminate the need for custom development, with delivery cycles for small to medium batch orders in just 3-5 days, far faster than specialty PCBs;
· A wide selection of suppliers: Tens of thousands of standard PCB manufacturers worldwide, ranging from large factories to small workshops, provide ample room for negotiation for buyers;
· Convenient after-sales service and maintenance: Standard PCBs offer low costs for fault detection and replacement, allowing maintenance personnel to quickly identify circuits and replace components, reducing equipment maintenance costs.
Low-barrier design and production
Low design threshold: Engineers do not need to master the characteristics of special substrates; ordinary electronic engineering knowledge is sufficient to complete the design. Low production threshold: Small and medium-sized factories can also achieve mass production through standardized equipment without high equipment investment, further driving down costs.
Rigid RPCB Manufacturing Capability
| Item | RPCB | HDI | |||
| minimum linewidth/linespacing | 3MIL/3MIL(0.075mm) | 2MIL/2MIL(0.05MM) | |||
| minimum hole diameter | 6MIL(0.15MM) | 6MIL(0.15MM) | |||
| minimum solder resist opening (single-side) | 1.5MIL(0.0375MM) | 1.2MIL(0.03MM) | |||
| minimum solder resist bridge | 3MIL(0.075MM) | 2.2MIL(0.055MM) | |||
| maximum aspect Ratio (thickness/hole diameter) | 0.417361111 | 0.334027778 | |||
| impedance control accuracy | +/-8% | +/-8% | |||
| finished thickness | 0.3-3.2MM | 0.2-3.2MM | |||
| maximum board size | 630MM*620MM | 620MM*544MM | |||
| maximum finished copper thickness | 6OZ(210UM) | 2OZ(70UM) | |||
| minimum board thickness | 6MIL(0.15MM) | 3MIL(0.076MM) | |||
| maximum layer | 14 layer | 12 layer | |||
| Surface treatment | HASL-LF、OSP 、Immersion Gold、 Immersion Tin 、Immersion Ag | Immersion Gold、OSP、selectiveimmersion gold、 | |||
| carbon print | |||||
| Min/max laser hole size | / | 3MIL / 9.8MIL | |||
| laser hole size tolerance | / | 0.1 |