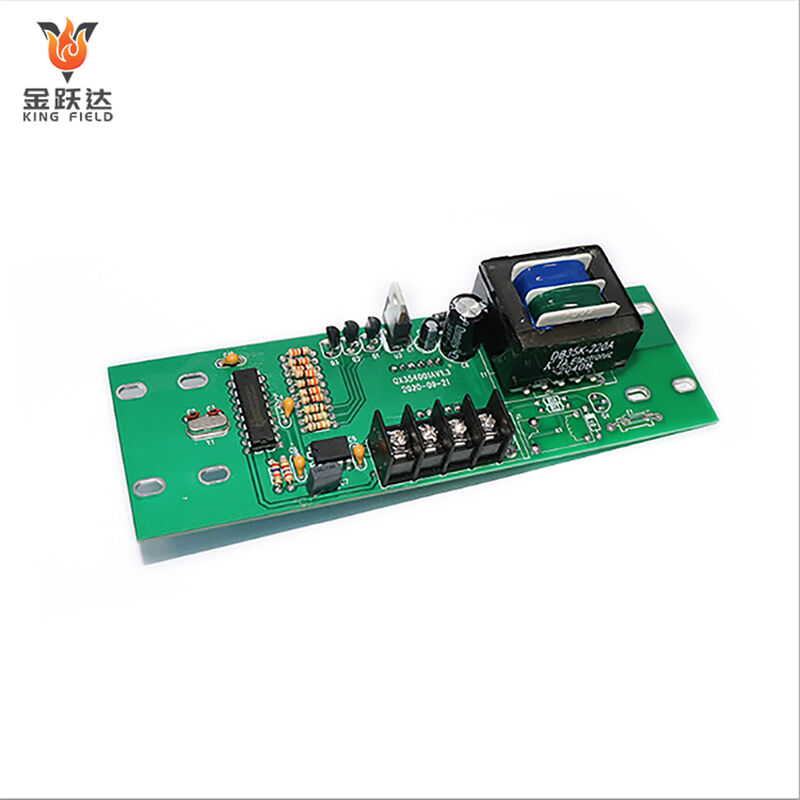
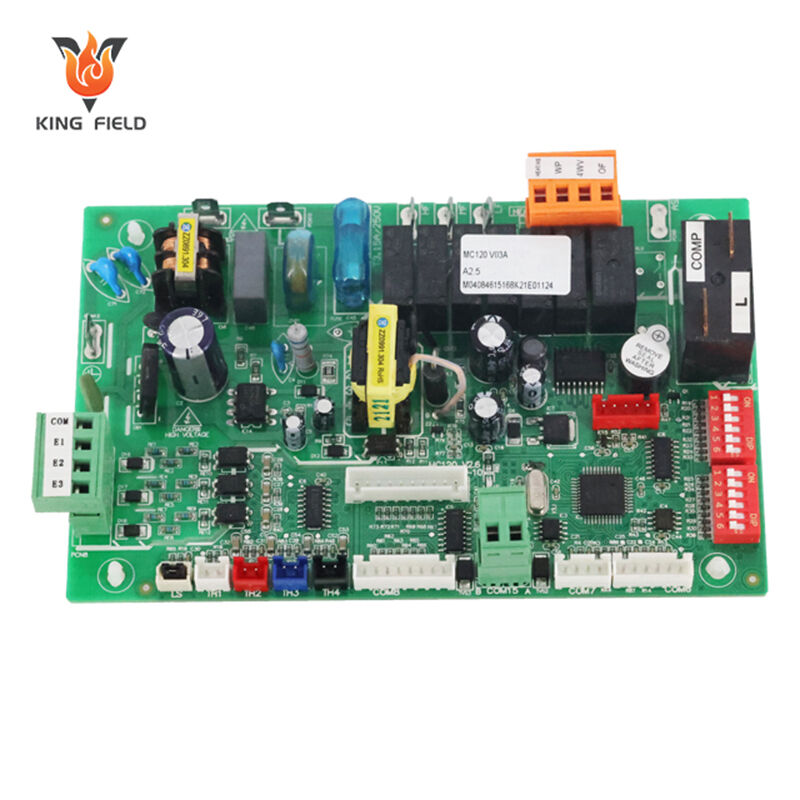
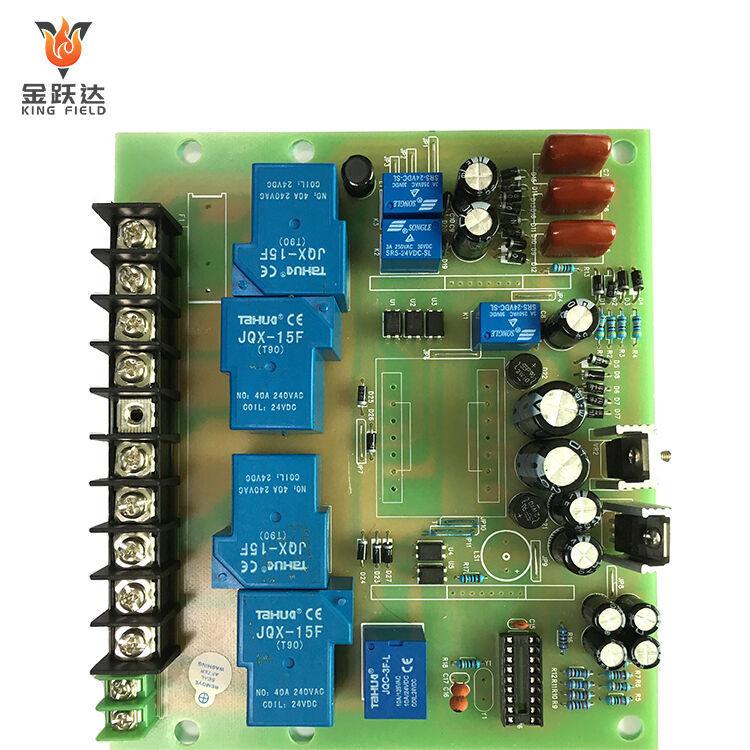
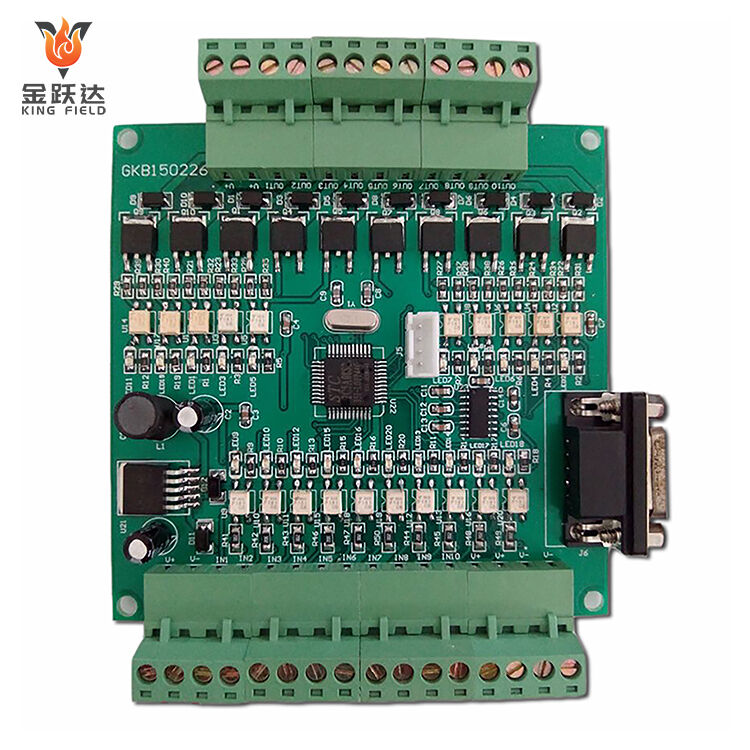
PCB Assembly Service
Reliable PCB Assembly for medical, industrial, automotive & consumer electronics. 24h prototyping, fast delivery, BOM matching, DFM analysis & AOI/ICT testing. Precision SMT/BGA assembly—consistent quality for your R&D and production needs.
✅ 24h rapid prototyping
✅ SMT/BGA assembly expertise
✅ Full testing & DFM support
Description
What is PCB Assembly service?
PCB Assembly Service is the professional service of mounting and soldering electronic components onto bare PCBs to build functional circuit assemblies, covering component sourcing, assembly, testing, and quality control, which is essential for electronics manufacturing. It is often offered by EMS providers, and is also known as PCBA services.
For electronics manufacturers, R&D teams, and procurement specialists, understanding PCBA is critical to selecting the right manufacturing partner.
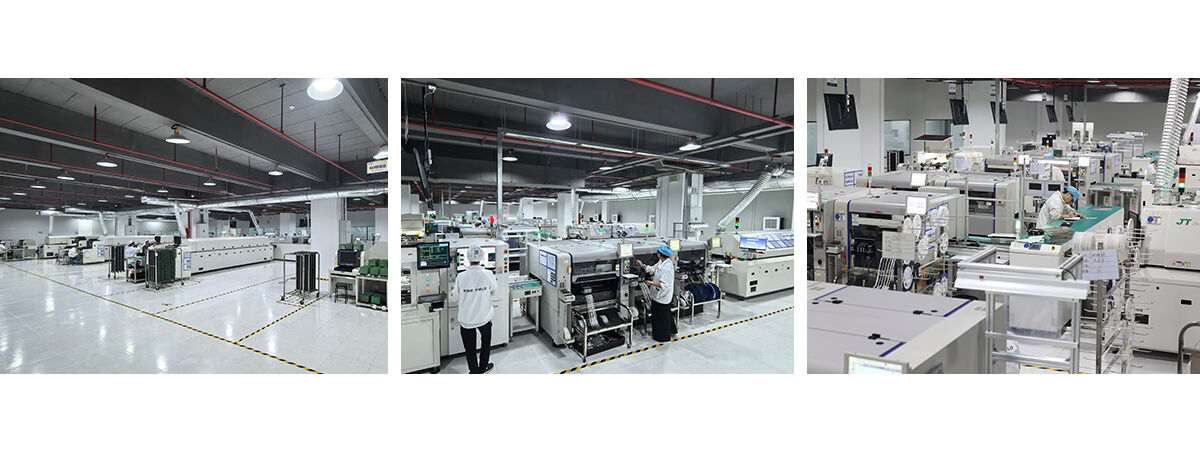
KING FIELD--PCB assembly plant
Our state-of-the-art PCB assembly plant boasts seven high-speed SMT production lines, equipped with state-of-the-art placement machines, reflow ovens, and comprehensive testing equipment. We possess full capabilities from prototype assembly to high-volume production, handling a wide range of components from passive components to large BGAs and connectors. Our assembly services include SMT, THT, hybrid technologies, complete assembly, and turnkey solutions encompassing component sourcing, testing, and logistics support.

Core Definition: Bare PCB vs. PCBA
| Bare PCB | PCBA | ||||
| A blank circuit board with copper traces, pads, and holes. | A functional assembly where all required components are soldered/mounted to the bare PCB. | ||||
| Purpose: Provides the "base" for electrical connectivity. | Purpose: Powers electronic devices. |
Key Stages of PCB Assembly
Kingfield follows global electronics assembly standard to ensure consistency and reliability. Below are the core steps:
Step 1: Component Preparation & Verification
·Component Sourcing: Use genuine, traceable components from authorized suppliers.
·Inspection: Check component values, packaging, and quality to avoid defects.
·Kitting: Organize components by assembly order for efficient production.
Step 2: Solder Paste Application
·Process: Use a stencil printer to apply precise amounts of solder paste to the PCB’s component pads.
·Kingfield Advantage: High-precision stencils for micro-components and consistent paste deposition.
Step 3: Component Placement
·SMT: Most common—automated pick-and-place machines mount tiny surface-mount components onto the PCB’s top/bottom layers.
·Through-Hole Technology: For larger, heavier components—components are inserted through holes in the PCB.
·Accuracy: Kingfield uses high-speed pick-and-place machines with ±0.03mm precision for dense layouts.
Step 4: Soldering
·Reflow Soldering (for SMT): The PCB passes through a reflow oven to melt the solder paste and bond components to the pads.
·Wave Soldering (for THT): The PCB is passed over a wave of molten solder to solder through-hole components.
·Kingfield Control: Lead-free solder options and real-time temperature profiling to prevent component damage.
Step 5: Inspection & Testing
·AOI: Cameras detect soldering defects.
·X-Ray Inspection: For hidden joints or multi-layer PCBs.
·ICT: Verifies electrical connectivity and component functionality.
·Functional Testing: Validates the PCBA’s performance under real operating conditions.
Step 6: Cleaning & Final Finishing
Remove excess solder flux with ultrasonic cleaning or aqueous cleaning.
Optional: Conformal coating to protect the PCBA from moisture, dust, or vibration.
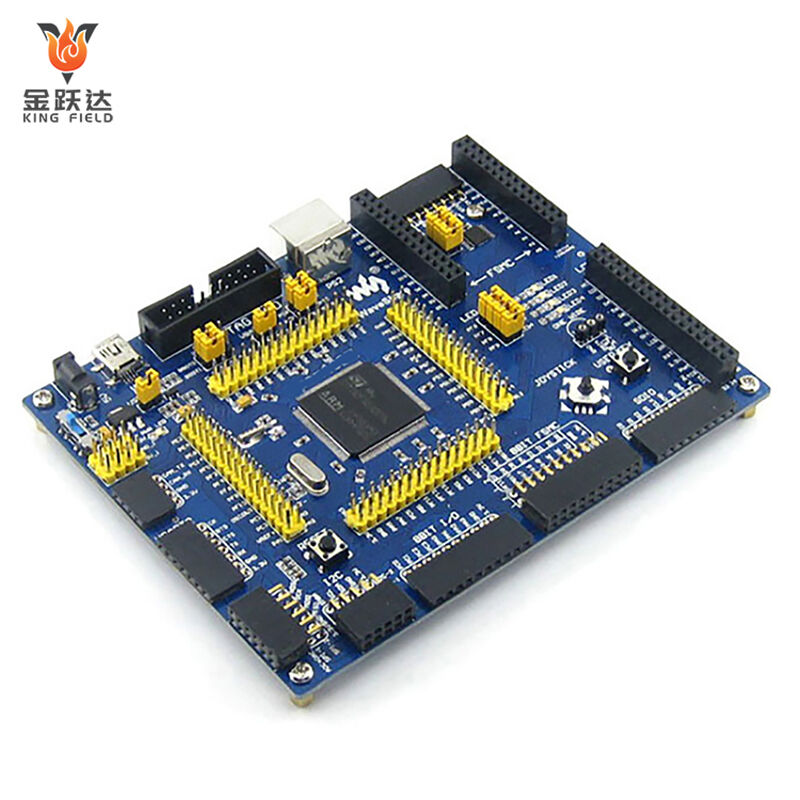
Types of PCB Assembly services
| Assembly Type | Description | Key Applications | |||
| SMT Assembly | Mounts surface-mount components. | Smartphones, wearables, IoT devices, industrial controls. | |||
| THT Assembly | Uses through-hole components. | Power supplies, automotive connectors, ruggedized industrial equipment. | |||
| Mixed-Technology Assembly | Combines SMT and THT for complex designs. | Medical devices, consumer electronics, industrial sensors. | |||
| Flexible PCB Assembly | Assembles components on bendable polyimide (PI) substrates. | Wearables, automotive dashboards, foldable electronics. | |||
| Rigid-Flex PCB Assembly | Combines rigid and flexible sections for 3D integration. | Aerospace avionics, automotive sensor modules, compact IoT devices. | |||
Why PCBA Matters
· Functionality: Without assembly, a bare PCB cannot power electronic devices—PCBA is the bridge between design and real-world use.
· Reliability: Precision assembly (per IPC standards) ensures long-term performance, reducing field failures and warranty claims.
· Cost Efficiency: Partnering with an experienced manufacturer avoids rework, minimizes material waste, and scales production.
· Customization: PCBA can be tailored to your device’s unique requirements.
Kingfield’s PCBA services Advantages
· Full Turnkey Solutions: From component sourcing and PCB fabrication to assembly, testing, and delivery.
· Advanced Capabilities: Supports micro-component assembly (01005, 0201), BGA/QFN soldering, and lead-free/RoHS-compliant processes.
· Quality Assurance: 100% inspection (AOI + X-ray + functional testing) and ISO 9001/IPC-A-610 certified production.
· Fast Lead Times: 3–15 business days for prototypes and high-volume runs.
Whether you need prototypes for R&D or mass production for consumer/industrial devices, Kingfield’s PCBA services are engineered to meet your technical specs and timeline. Contact our team to discuss your project!

Manufacturing capacity
| Equipment manufacturing process capability | |||||
| SMT Capacity | 60,000,000 chips/day | ||||
| THT Capacity | 1.500,000 chips/day | ||||
| Delivery Time | Expedited 24 hours | ||||
| Types of PCBs Available for Assembly | Rigid boards, flexible boards, rigid-flex boards, aluminum boards | ||||
| PCB Specifications for Assembly |
Maximum size: 480x510 mm; Minimum size: 50x100 mm |
||||
| Minimum Assembly Component | 01005 | ||||
| Minimum BGA | Rigid boards 0.3 mm; Flexible boards 0.4 mm | ||||
| Minimum Fine-Pitch Component | 0.2 mm | ||||
| Component Placement Accuracy | ±0.015 mm | ||||
| Maximum Component Height | 25 mm | ||||
Case Studies
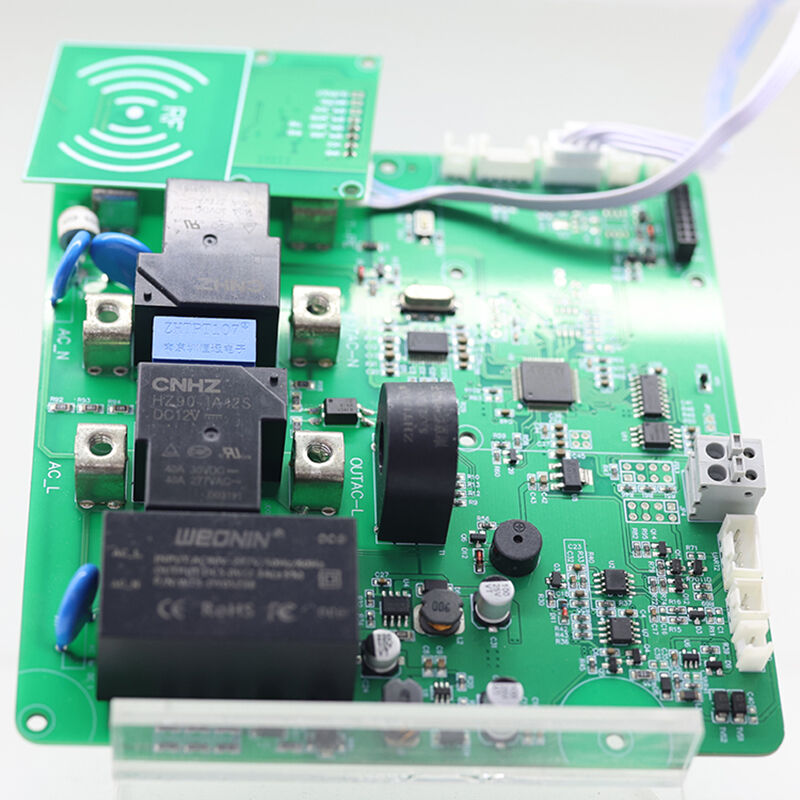 |
 |
 |
|||
| New Energy PCBA | Industrial Control PCBA | Automotive motor PCBA |
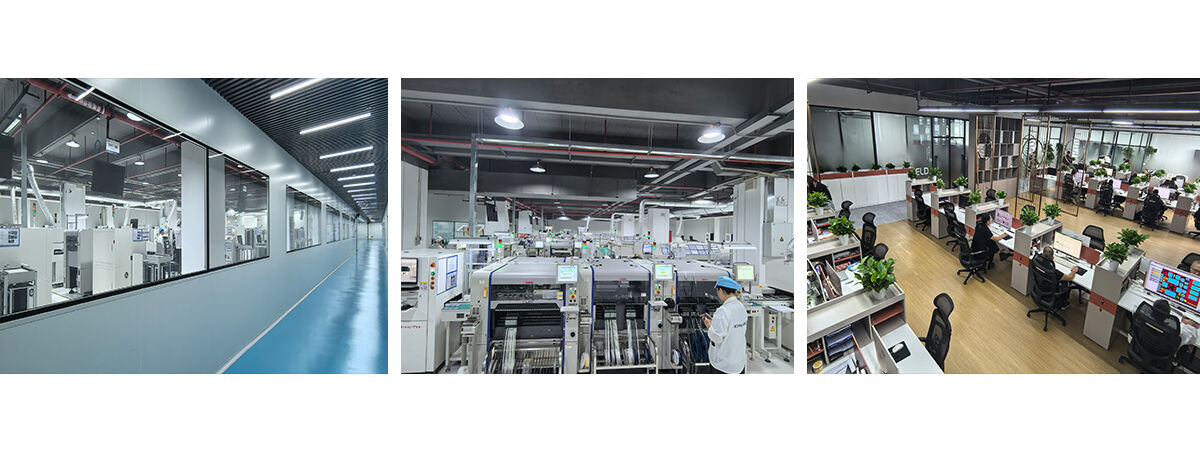
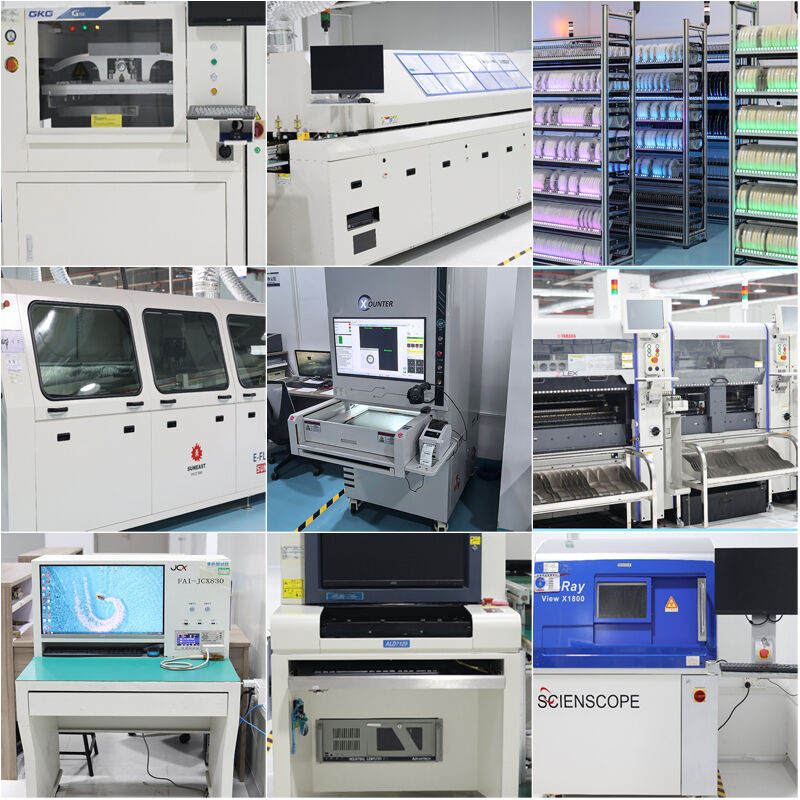
Equipment display
Equipment display

FAQ
Q: How to avoid component misalignment during assembly?
A: Root cause: Machine calibration errors, PCB warpage. Solution: Daily machine calibration, rigid PCB fixtures, pre-soldering AOI inspections.
Q:What is the difference between PCB and PCBA?
A:PCB is an abbreviation for printed circuit board, and when we refer to it, it usually means bare board.
PCBA board is a rigid body of a PCB with various electronic components and is typically green in color, they consist of a fiberglass substrate, electronic components, conductive traces on copper layers, holes in which the components are fitted, and different layers.
Q:Why have to assemble a printed circuit board?
A;We believe that PCB bare board is unable to function effectively until they are assembled into PCBA board to fulfill their intended purpose in electronics. You can tailor the circuit design according to your specific requirements. Once the printed circuit board assembly is complete, the conductive traces on the PCB facilitate the transmission of digital, high-speed, or analog signals between different points, enabling the desired functionality.
Q:Why use automated PCB assembly?
A:Prior to the advent of pick-and-place robots, the task of component placement was typically performed manually by technicians using tools like tweezers to carefully position each component onto the designated location on the PCB. However, this manual process was time-consuming and labor-intensive, often leading to longer lead times, increased eye strain, and fatigue among technicians.
To address these challenges and enhance the efficiency of PCB assembly and manufacturing, pick-and-place robots were introduced. These automated robotic systems revolutionized the industry by streamlining the component placement process. By utilizing programmed instructions and advanced machine vision systems, pick-and-place robots can accurately and swiftly position components onto the PCB with precision.
Q:Is a reflow oven necessary in a PCB assembly line?
A:A crucial element in the SMT assembly process is the use of commercial reflow ovens. These ovens employ a controlled heating and cooling cycle to securely attach components to the PCB. When selecting a service provider, it is advisable to consider the temperature zones of their equipment.
For hobbyist projects or small-scale assembly, a soldering iron can be utilized for soldering tasks. This handheld tool allows precise application of heat to melt solder and establish electrical connections between components and the PCB.