Medical PCB assembly allows no shortcuts—precision, reliability, and global standards compliance are non-negotiable for patient safety and clinical innovation, as these components power critical devices like imaging systems and ventilators.
“The quality, reliability, and precision of your medical PCBA can have a direct impact on patient health, long-term trust, and regulatory approval for your medical device.” – Alexander Price, MedTech Product Lead
Far stricter than consumer/industrial electronics, medical PCB assembly demands rigorous design, materials, testing, traceability, and documentation (ISO 13485, FDA). Failure risks are catastrophic, driving reliance on specialized turnkey PCB assembly experts.
Medical PCB assembly is the specialized process of mounting, soldering, and testing electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) destined for use in medical devices. This essential step transforms a bare PCB into an intelligent, functional module that powers healthcare instrumentation, monitoring systems, implantable devices, and more.
At its core, the PCB assembly (PCBA) process for medical devices involves several highly controlled steps:
Design Review and DFA (Design for Assembly):
Collaboration between OEM engineers and the PCBA manufacturer to optimize for manufacturability and regulatory compliance.
Use of a DFM checklist for medical devices ensures every PCB is assembly-ready from day one.
Solder Paste Application (Stencil Printing):
Ultra-fine 4-mil trace/space capability enables precise layout, supporting miniaturization and high-density integration essential for wearables and implantables.
Pick and Place Assembly:
Automated machines place micro-components—such as BGA, QFN, and leadless packages—with sub-millimeter accuracy.
Soldering:
SMT assembly and reflow are standard for surface-mount parts, while through-hole technology (THT/PTH) is reserved for robust or high-current connections.
Selective wave soldering and mixed technology assembly are frequently used for hybrid medical circuits.
Inspection and Quality Control:
Processes include automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection (for BGAs), and in-circuit test (ICT testing) to verify assembly integrity.
Functional testing (FCT) ensures the board works as intended before it ever reaches a device.
Final Cleaning and Sterilization Prep:
Medical PCBs often require pre-sterilization cleaning to remove all flux residues and contaminants, reducing risk for infection or device malfunction.
SMT assembly is the dominant method in modern medical PCBA. Tiny components are placed directly onto the PCB surface, enabling:
While SMT is suited to most modern electronics, THT is still invaluable in some medical applications requiring:
|
Step |
Description |
Key Technologies |
|
DFA & DFM Review |
Ensures manufacturability, regulatory compliance |
Software tools, checklists |
|
Solder Paste Application |
Printed with high precision |
SMT stencil printing, ultra-fine traces |
|
Pick & Place Assembly |
Automated placement of components |
High-speed SMT machines, accuracy to 20μm |
|
Soldering |
Secures components, ensures reliability |
Reflow oven, selective wave soldering, THT |
|
AOI/X-Ray/ICT Testing |
Verifies solder joints, connections, and circuits |
AOI cameras, X-ray systems, ICT fixtures |
|
Functional Testing (FCT) |
Simulates real-world operation |
Custom test fixtures, data acquisition systems |
|
Cleaning & Sterilization |
Removal of flux, prep for clinical environments |
Aqueous cleaning, ion residue tests, ISO 10993 prep |
Medical PCB assembly services are not simply about soldering tiny chips. They demand:
Miniaturization: Enables next-gen wearable and implantable devices. Ultra-fine 4-mil trace/space and high-density SMT assembly allow for more features in less space.
Enhanced Data Processing: Faster, smarter data sharing (real-time wireless transmission, edge analytics) improves timely clinical decisions.
Biocompatibility: Use of medical-grade materials (PEEK™, polyimide, PTFE) enables safe, long-term patient contact and repeated sterilization.The flexibility to deliver everything from urgent PCB prototype quotes to small/medium batch production—with instant turnaround and trusted support
Medical electronics stretch far beyond the confines of hospitals. The versatility of medical PCB assembly enables breakthroughs across clinical, diagnostic, therapeutic, and wearable technologies. As the demand for smarter healthcare devices grows, partnering with an experienced medical PCB manufacturer ensures your innovations are built on a foundation of reliability, compliance, and engineering excellence.
A global medical technology company required a rigid-flex PCB assembly for a dermatological laser therapy device. The solution needed superior thermal management, miniaturized high-speed digital signals, and biocompatible materials suitable for close skin contact. Our engineering team designed a prototype PCBA using polyimide flex and ceramic layers, verified all SMT assembly joints with AOI and X-ray inspection, and delivered functional units within a 24-hour fast turnaround for clinical trial use.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, our ISO 13485 certified EMS team supported a rapid scale-up of ventilator PCB assembly for ICU use. By leveraging turnkey PCB assembly (including component sourcing, DFA, and mass reflow soldering of ultra-fine pitch microcontrollers), we ensured robust supply, rapid deployment, and 99.6% on-time delivery reliability—even as global supply chains were strained.
|
Device/Application |
PCB Technology Used |
Key Challenges |
Solution Highlights |
|
Wearable Glucose Monitor |
Rigid-Flex, SMT, BGA |
Sweat/contamination, size, EMC |
Biocompatible flex, conformal coating, AOI test |
|
Digital X-Ray Detector |
HDI, Multilayer (12-layer) |
Signal integrity, high voltage |
Stackup optimization, ICT & FCT testing |
|
Infusion Control Panel |
Rigid FR-4, THT, relays |
Reliability, mixed voltages |
Selective soldering, stringent QA, FAI |
Experience with lifecycle management
NPI (New Product Introduction) support through to mass-market scale-up
Handling both small batch prototype PCBA and large-scale turnkey production
Capability to handle varied technologies
SMT, through-hole, rigid-flex, ceramic, HDI, and microcircuit assembly under one roof
Proven track record across device types
More than 120,000 global PCB assembly projects delivered for medical, dental, and therapy equipment
Serving firms from medtech startups to established global brands
The path from medical product concept to reliable, compliant device is filled with technical hurdles and regulatory benchmarks. To bridge these challenges, top medtech companies partner with experienced, certified turnkey PCB assembly providers offering start-to-finish capabilities. “Turnkey” means your PCBA supplier manages everything—PCB manufacturing, component sourcing, assembly, testing, documentation, and even logistics.
Choosing a turnkey PCB assembly service has profound advantages for medical OEMs and startups:
With over 15 years of experience and a team of 200+ highly skilled engineers, our medical PCB assembly services tackle the most demanding requirements—no matter the batch size or complexity.
Prototype PCB assembly is the foundation of every medical device lifecycle. A robust prototyping process gives you:
|
Core Capability |
Benefit for Medical Device Production |
|
In-House Stencils & MES |
Shortens lead times for design updates/NPI |
|
16 SMT Lines/Hybrid Tech |
Handles high-mix, complex medical assemblies |
|
Prototype to Production Flow |
Change seamlessly from “one-off” to scaled production |
|
Engineering & Compliance Team |
Ensures documentation, traceability, and regulatory audit support |
Market success requires global compliance—ISO 13485-certified PCB partners enable smooth audits, mitigate risks, and ensure manufacturing/testing align with global regulatory and user standards.
|
Certification |
Relevance & Benefits |
|
ISO 9001 |
Defines general quality management, emphasizing process control and continuous improvement. |
|
ISO 13485 |
Specifies requirements for medical device quality management: traceability, risk mitigation, validation |
|
IATF 16949 |
Automotive but relevant for mission-critical QA and process discipline. |
|
ISO 14001 |
Environmental management—demonstrates responsible, sustainable manufacturing. |
|
UL |
Guarantees electrical safety and fire resistance in finished assemblies. |
|
RoHS & REACH |
Ensures restriction of hazardous substances, environmental compliance, and EU marketability. |
|
ESD Management |
Protects sensitive components from electrostatic discharge, critical for reliability. |
|
FDA, CE, IEC60601 |
Regulatory benchmarks for U.S., Europe, and global medical device markets. |
Building a medical PCB isn’t just about putting components on a board. It’s about creating a robust, repeatable, and fully documented process that transforms a design file into a safe, durable, and flawless product—every single time.
Each assembly lot is logged with a unique identifier, batch data, process parameters, test outcomes, and operator information. This digital record ensures:
FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (US): Medical device quality system regulation
CE Mark (Europe): Safety and performance per EU requirements
IEC 60601 series: Basic safety and essential performance for medical electrical equipment
Quality Control Equipment & Techniques
|
QC/Test Technique |
Purpose |
Typical Equipment/Standards |
|
AOI |
Visual inspection |
High-res cameras, inline AOI, IPC-A-610 |
|
X-ray |
Internal solder/joint checks |
2D/3D X-ray, automated defect recognition |
|
FCT |
Simulate real use |
Custom test fixtures/benches, data logging |
|
ICT |
Electrical property validation |
Bed-of-nails tester, Flying Probe, PC-based |
|
Environmental Test |
Endurance/safety verification |
Temp chambers, salt spray, drop testers |
|
SPI |
Paste print accuracy |
Inline SPI scanners, image analysis |
|
FAI |
Production validation |
Full measurement labs, QMS databases |
|
Testing Type |
Purpose and Benefits |
Industry Keywords/Standards |
|
Flying Probe Test (FPT) |
Non-contact, needle-based test for shorts, opens, and layout errors—ideal for prototypes/NPI. |
IPC-9252, fast prototype TAT |
|
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) |
High-speed cameras detect missing, misaligned, or misoriented parts post-assembly. |
SMT/THT AOI, IPC-A-610 |
|
X-ray Inspection |
Views internal connections (e.g., BGA, QFN), hidden cold joints or solder voids. |
BGA, micro-BGA, CT scanning |
|
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) |
Electrical test of populated PCB—measures continuity, resistance, capacitance, presence of defects. |
Bed-of-nails, Flying Probe ICT |
|
Functional Testing (FCT) |
Simulates real-world operation to ensure device logic, safety, and communication all work together. |
IEC 60601 test, customer-specific rigs |
|
Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) |
Validates even, accurate application of solder paste before pick-and-place. |
Inline SPI, stencil print QA |
|
First Article Inspection (FAI) |
Full validation and documentation of the initial assembly against design specs. |
FAI report, batch record |
|
Environmental/Aging Tests |
Simulates harsh real-world use: temperature cycling, drop, humidity, chemical exposure, aging. |
IEC, ISO, ASTM, medical industry norms |
Regulations for medical electronics extend beyond the physical board and deep into production protocols and documentation. ISO 13485, ISO 9001:2015, IATF 16949, ISO 14001:2015, and UL are foundational, but many projects must also conform to:
Maximum test coverage (key for ICT and FCT accessibility)
Elimination of “test-point shadows” (areas not testable by AOI or flying probe)
Placement of accessible fiducials and test pads for faster, lower-cost NPI quoting
Proactive manufacturers offer a DFM/DFT review as part of their value-added services or as a stage-gate for every new design. This review optimizes the board layout to allow:
The journey from concept to successful clinical deployment begins with robust PCBA prototyping for medical devices. For medical innovators, a prototype is not simply a working proof-of-concept—it's a regulatory, functional, and manufacturability checkpoint that ultimately dictates device safety, speed-to-market, and total costs.
Unlike in general electronics, the stakes in medical device prototyping are particularly high:
Modern online quoting tools make securing a PCB prototype quote almost instant—if your project documentation is complete. For accurate pricing and a fast turnaround, you’ll typically need:
|
File Type |
Description |
Why It’s Needed |
|
Gerber |
PCB stack-up, copper, mask |
Board fabrication |
|
BOM |
All components, alternates |
Sourcing, pricing |
|
Pick-and-Place |
Placement coordinates, values |
SMT automation |
|
Assembly Drawing |
Location, orientation info |
Assembly clarity |
|
Test Instructions |
Special QA requirements |
PCBA validation |
The process of medical PCB assembly turns raw design files into life-saving electronic modules—each step blending precision engineering, compliance, and rapid, quality-controlled execution. Understanding this assembly journey helps you prepare accurate documentation (for faster, more competitive PCB assembly quotes), set realistic PCB assembly lead times, and streamline both development and regulatory approvals.
|
Assembly Step |
Tools/Tech Used |
Compliance/Standard |
Impact on Quality |
|
DFM, DFA, DFT |
Engineering review, software tools, checklists |
IPC-2221, IEC 60601 |
Yields, quote speed, audit readiness |
|
Solder Print/SPI |
Stencil printer, inline SPI |
IPC-6012, ISO 13485 |
Solder defect catch, reduce rework |
|
SMT/THT Assembly |
High-precision placers, reflow, wave solder |
SMT, THT, auto/robot pick |
Enables fine-pitch/high layer PCBs |
|
AOI/X-ray/ICT/FCT |
AOI systems, 2D/3D X-ray, bed-of-nails/fl. probe |
IPC-A-610, FDA, IEC tests |
QA, regulatory documentation, reliability |
|
Aging/Env. Test |
Burn-in ovens, climate chambers, vibration rigs |
ISO, ASTM medical standards |
Ensures device reliability, lifespan |
|
Quote Element |
Details Provided |
Impact on Cost/Lead Time |
|
PCB Fabrication Specs |
Material (FR-4, flex, ceramic, etc.), layers, finish, UL/medical standards |
High-layer/complex boards raise cost |
|
Component Sourcing |
Vendor quote for BOM, availability, alternates |
Market pricing, shortages, substitutes |
|
Assembly Type |
SMT, THT, mixed; leadless/BGA parts, quantity |
Fine-pitch/complex boards: higher setup |
|
Testing/Inspection |
AOI, X-ray, FCT, ICT, FAI, custom protocols |
Required for ISO 13485, cost varies |
|
Certifications/Compliance |
RoHS, REACH, UL; ISO audit traceability |
Medical compliance adds value for audits |
|
Delivery/Logistics |
Turnaround options (24 hr–4 wk), shipping, tracking |
Express builds/priority shipping cost more |
|
Attribute |
Supplier A |
Supplier B |
Supplier C |
|
PCB Material |
FR-4, ISO 13485 |
Polyimide, RoHS |
FR-4, ISO 9001 |
|
Assembly Type |
Full Turnkey SMT/THT |
Partial (no components) |
Turnkey + DFM |
|
Testing Included |
AOI, X-ray, FCT |
AOI Only |
AOI, ICT, SPI |
|
Certs/Docs |
ISO 13485, UL, RoHS |
RoHS |
ISO 9001, RoHS |
|
Lead Time |
7 working days |
14 working days |
10 working days |
|
Price per Board |
$38.70 |
$31.40 |
$40.25 |
|
Warranty/Support |
12 months, NPI help |
6 months |
12 months |
|
TCO Factor |
Risks of Ignoring |
How Good Suppliers Mitigate |
|
Quality Failures |
Repairs, recalls, patient risk |
Robust QA, complete traceability, warranty coverage |
|
Documentation Gaps |
Regulatory rejection, delays |
Standard batch records, test certificates, ISO docs |
|
Delivery Performance |
Project delays |
Real-time MES tracking, guaranteed ship dates |
|
Engineering Support |
Unforeseen errors/Redesign |
DFM, DFT, DFA checklist, early feedback/free review |
|
Compliance Readiness |
Market bans, repeats audits |
Upfront compliance, pre-filled regulatory reports |
Rigid FR-4: Standard for medical monitors, diagnostic boards, and most general devices—low-to-medium cost.
Polyimide & Rigid-Flex: Essential for wearables and implants (flexibility, biocompatibility, repeated sterilization)—higher raw cost, more complex assembly.
Ceramic or PTFE Substrates: Required for imaging (X-ray/CT/MRI), RF, or extremely high-reliability apps—premium pricing, but with critical performance benefits.
Aluminum MCPCB: Used where heat dissipation is vital, raising both the manufacturing and handling cost.
Layer Count: More layers (6–12 for high-density PCBs) increases cost exponentially due to more passes, lamination, and inner layer inspection.
Ultra-fine Features: 4-mil trace/space, microvias, blind/buried vias, and BGA/micro-BGA pads require state-of-the-art machinery; higher yield loss risks.
Size and Shape: Odd shapes, cutouts, or ultra-miniaturized profiles add handling, setup, and potential assembly cost.
Customer: CardioTech Innovations (MedTech Startup) Application: Wearable ECG and arrhythmia monitoring Challenge: Miniaturization, rapid FDA pretrial approval, ultra-fine trace design, short lead time
Solution: CardioTech required a rigid-flex PCB assembly with biocompatible conformal coating, micro-BGA placement, and robust DFM for wireless transmission reliability. Leveraging our rapid PCBA prototyping service, they:
Customer: Global Medical Device Manufacturer Application: ICU/Emergency ventilators Challenge: Pandemic-induced supply chain shortages, absolute delivery accountability, compliance documentation
Solution: We deployed our full turnkey PCB assembly service, covering everything from component sourcing/verification to batch traceability and expedited 24-hour builds.
Documented aging and environmental test results (humidity, hot/cold cycling)
Customer: VisionTech Diagnostics Application: Digital X-ray and CT imaging Challenge: 12-layer HDI PCB, signal integrity, environmental/longevity testing
Solution: Our engineering team provided:
Full traceability and compliance packs (ISO, UL, RoHS docs)
Batch-level test reports: AOI, X-ray, ICT, FCT, FAI
Before opening a quoting portal, gather these standard files for upload:
Gerber Files (.zip): All PCB layers, drills, mask, silkscreen, and board outline
Bill of Materials (BOM): Itemized part numbers, manufacturers, and suggested alternates for key components (critical for supplies in tight medical markets)
Pick-and-Place File (Centroid): X/Y coordinates, rotation, and value for automated pick and place
Assembly Drawings & Special Instructions: Details for orientation, no-placement zones, keep-out areas, hand or selective soldering, or special finishes (such as conformal coating or sterilization-ready prep)
Testing Requirements: Specific in-circuit or functional testing steps; note any ICT, FCT, or aging test mandates
|
Quote Parameter |
Example Option |
Impact on Price |
|
Qty |
10, 100, 1,000 |
Volume discounts |
|
Layers |
2, 4, 6, 12 |
Higher complexity |
|
Assembly |
SMT only, THT, mixed |
Changeover/setup cost |
|
Testing |
AOI standard, +ICT/+FCT/X-ray |
Adds cost, ensures QA |
Once your files and parameters are submitted, most suppliers:
The best quoting tools: Instantly update price and lead time estimates as you tweak design, volume, or testing requirements—giving you price/performance flexibility before commitment.
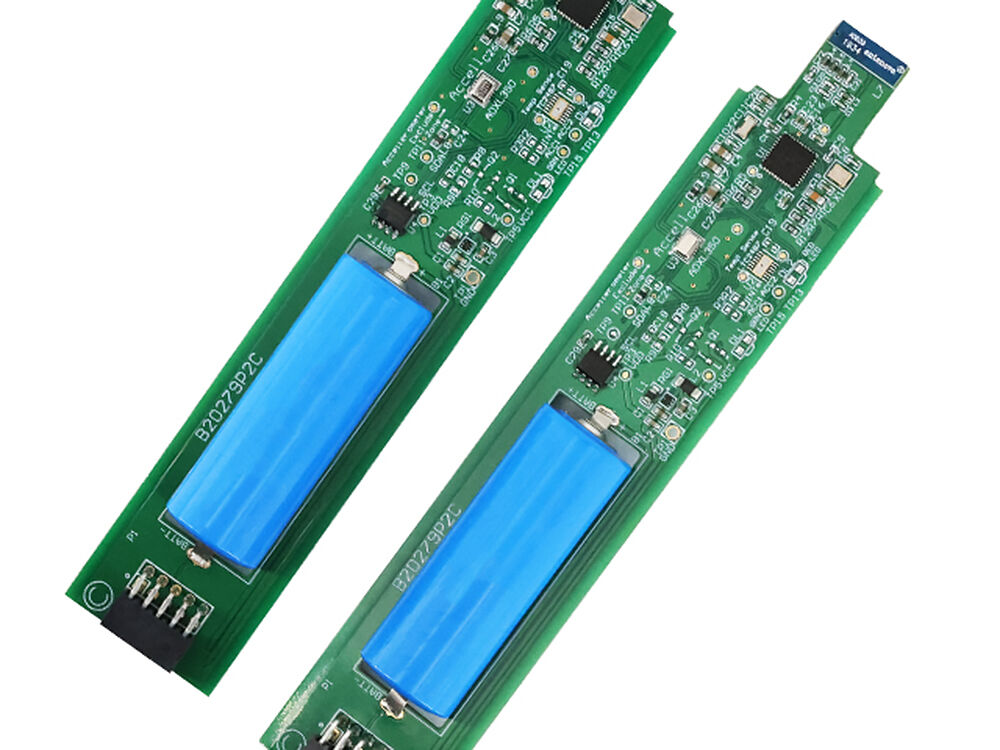

Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is the process of mounting, soldering, and testing electronic components on a bare PCB, turning it into a functional electronic circuit. For medical devices, PCBA’s importance is elevated because:
Higher costs stem from: strict regulatory/documentation overhead; comprehensive testing; expensive medical-grade materials/components; mandatory traceability/batch control; built-in certification/audit readiness.
Lead time depends on: accurate engineering files/BOMs; component availability; value-added services (testing/certifications); project type (prototypes: 24–72hrs, production: 7–15 working days).
Top suppliers offer 0/low MOQ for prototyping; support 1–10,000 unit batches; provide high-volume options with supply chain support for large deployments.
 Hot News
Hot News2026-01-17
2026-01-16
2026-01-15
2026-01-14
2026-01-13
2026-01-12
2026-01-09
2026-01-08