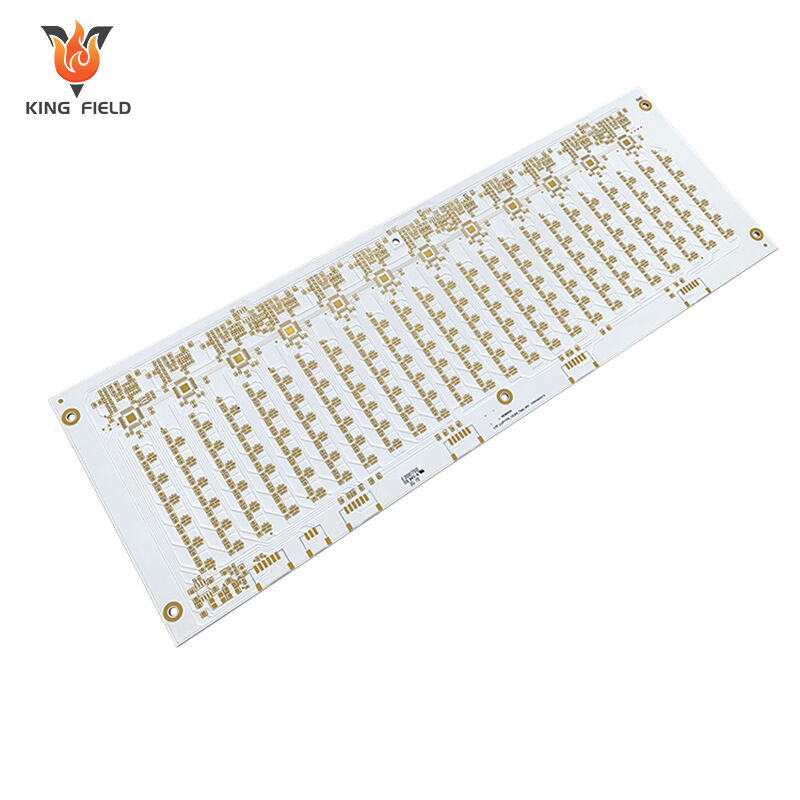
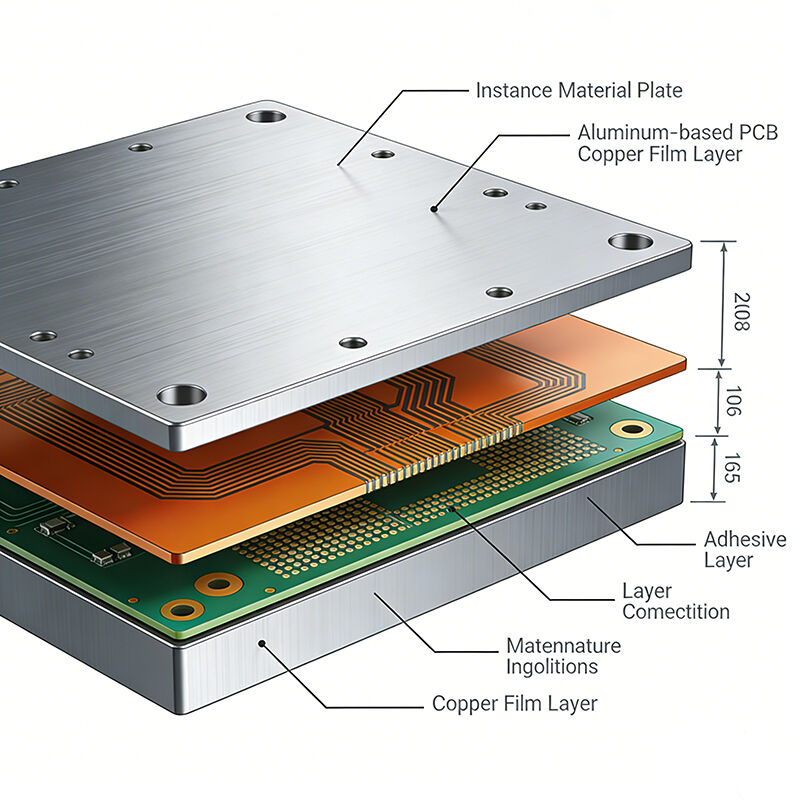
Aluminum PCB
High-performance Aluminum PCBs for medical, industrial, automotive & consumer electronics—specialized in thermal management for high-
power applications (LEDs, power supplies, automotive electronics). Superior heat dissipation, lightweight aluminum substrate, corrosion
resistance, and reliable conductivity paired with 24h prototyping, fast delivery, DFM support & AOI testing. Durable, thermally efficient, and
cost-effective for power-dense devices.
✅ Exceptional heat dissipation
✅ DFM optimization & quality validation
✅ LED/automotive/power electronics focus
Description
What is an aluminum PCB?
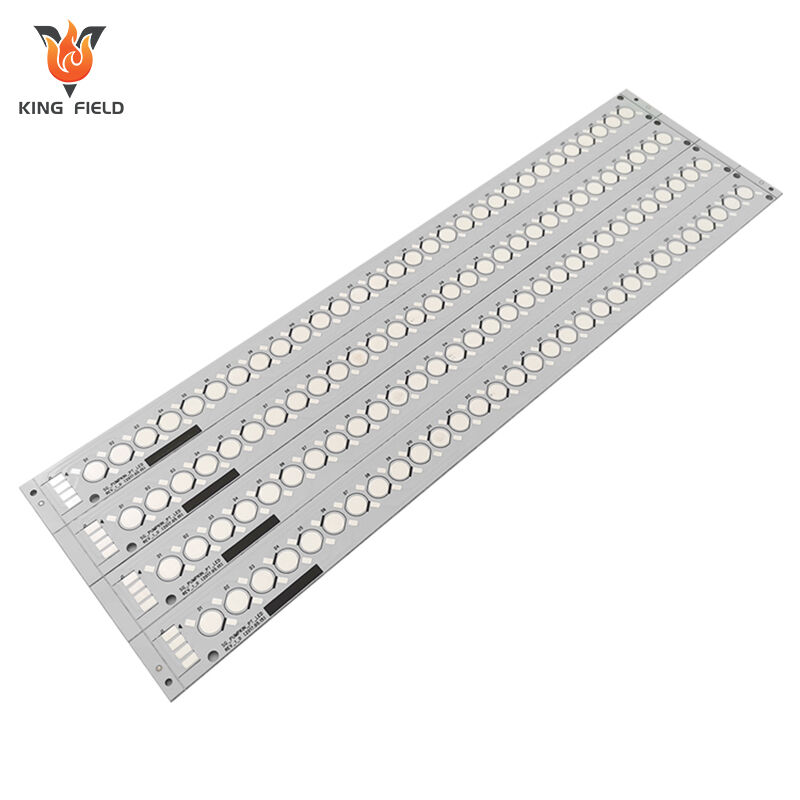
Aluminum PCB is a special type of PCB composed of an aluminum substrate, insulating layer and copper foil. Its core advantage lies in efficient heat dissipation, and it also features high mechanical strength, good electromagnetic shielding, environmental protection and energy conservation. It is suitable for high-power scenarios such as LED lighting and power electronics. Kingfield can provide customized design, prototyping and mass production services, support multiple thermal conductivity options and comply with IPC standards.
Aluminum core pcb, also known as metal core PCB or aluminum core PCB, is a circuit board with aluminum substrate. Unlike traditional FR4 fiberglass boards, this aluminum-based material has good thermal conductivity and can effectively conduct heat away from key components, thereby improving the stability and durability of the circuit board in high-power and high-temperature environments. Aluminum PCBs are widely used in fields with high thermal management requirements such as LED lighting, power modules, and automotive electronics.

Why is Aluminum Used in Circuit Boards?
Aluminum is used in circuit boards primarily for its superior thermal conductivity—far exceeding traditional FR-4 substrates—enabling efficient dissipation of heat from high-power components , reducing overheating risks and extending product lifespan. Additionally, it offers high mechanical strength, natural electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding to stabilize signal transmission, and eco-friendliness. These properties make it ideal for high-power, high-heat applications like LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power supplies. Kingfield leverages these advantages to provide customized Al-PCB solutions, supporting various thermal conductivity requirements and complying with IPC standards.
Types of Aluminum PCB
1. Classified by Insulation Layer Material
FR-4 aluminum printed circuit boards
Insulation layer: FR-4 epoxy resin material
Features: Low cost, medium thermal conductivity (1.0-2.0 W/(m·K))
Applications: Medium-to-low power scenarios Polyimide (PI) Aluminum PCB
Insulation layer: Polyimide
Features: High temperature resistance (-200℃~260℃), excellent thermal conductivity (2.0-4.0 W/(m·K))
Applications: High-temperature, high-power scenarios
Thermal Conductive Paste Aluminum PCB
Insulation layer: High thermal conductivity silicone
Features: High thermal conductivity (3.0-6.0 W/(m·K)), outstanding heat dissipation efficiency
Applications: High-power LEDs, inverters, and other high heat flux density equipment
2. Classified by Thermal Conductivity
| Type | Thermal Conductivity Range | Applications | |||
| Low Thermal Conductivity | 1.0-2.0 W/(m·K) | General LED lighting, low-power consumer electronics modules | |||
| Medium Thermal Conductivity | 2.0-4.0 W/(m·K) | Automotive electronics, medium-power power supplies, industrial control modules | |||
| High Thermal Conductivity | 4.0-6.0 W/(m·K) | High-power LED street lights, frequency converters, power amplifiers |
3. Classified by Structure
- Single-Sided Aluminum PCB
Structure: Single copper foil layer + insulation layer + aluminum substrate
Features: Simple structure, low cost
Applications: Simple circuits
- Double-Sided Aluminum PCB
Structure: Double copper foil layers + insulation layer + aluminum substrate
Features: Supports complex circuit layouts, uniform heat dissipation
Applications: Medium-power power supplies, automotive LED driver modules
- Multilayer Aluminum PCB
Structure: Multilayer copper foil + insulation layer + aluminum substrate
Features: High integration, supports high-density wiring
Applications: High-end automotive electronics, industrial high-power control equipment
Key Factors
Key factors in the manufacturing of aluminum-based printed circuit boards
| Key factors | Key Requirement | Key points of industry adaptation | |||
| Base material selection |
- Aluminum substrate types: Common aluminum substrate (FR-4 + aluminum core), high thermal conductivity aluminum substrate. Thermal conductivity: 1.0-10.0 W/(m · K) (matching as required) - Insulation layer thickness: 0.1-0.3mm (balancing heat conduction and insulation) |
Automotive/industrial control: High thermal conductivity (≥ 2.0W /(m · K)), temperature resistance -40 to 125℃; Medical: Biocompatibility + low EMI | |||
| Thermal insulation layer process |
- Bonding methods: Hot-press bonding (conventional), vacuum bonding (high-precision) - Materials: Epoxy resin (low cost), polyimide, ceramic |
Medical equipment: Halogen-free, low volatility; Consumer electronics: Thinning (≤0.15mm) | |||
| Precision of line fabrication |
- Line width/line spacing: minimum 0.1mm/0.1mm (standard), 0.075mm/0.075mm (high precision) - Copper foil thickness: 1-3oz (suitable for current requirements) |
Automotive/industrial control: High current circuits (2-3oz copper foil); Consumer electronics: High-density wiring (fine line width) | |||
| Heat dissipation structure design |
- Aluminum substrate thickness: 1.0-3.0mm (Enhanced heat dissipation) - Via design: Thermal conductive via (filled with conductive adhesive), heat dissipation window |
Power device PCBA: Thermal via spacing ≤5mm; Outdoor equipment: Aluminum-based grounding for surge protection | |||
| Welding and assembly compatibility |
- Surface treatment: Tin spraying (conventional), gold plating (high precision), OSP (environmentally friendly) - Solderability: 260℃/10s (three reflow ovens) |
Medical PCBA: Lead-free soldering (RoHS compliant) Automotive specification: No warping after high-temperature welding (flatness ≤0.1mm/m) |
|||
| Reliability testing standard |
- Electrical performance: Insulation resistance ≥10¹⁰Ω, breakdown voltage ≥2kV - Environmental testing: High and low temperature cycling (-40 to 125℃), damp heat aging (85% RH/85℃) - Mechanical test: Bending strength ≥50MPa |
Automotive grade: AEC-Q200 certification; Medical grade: ISO 13485 compliant; Industrial control: IP67 protection compatible |
The core advantages of aluminum printed circuit boards
| Advantageous category | core value | Industry application scenario matching | |||
| Ultra-high thermal conductivity |
· coefficient of thermal conductivity of 1.0-10.0 W/(m, K), far higher than 0.3 FR - 4-0.5 W/(m K)) · Quickly dissipate the heat of power devices and reduce the chip temperature by 20-50℃ |
Automotive-grade power modules, industrial control high-power inverters, and medical equipment power units | |||
| Excellent heat dissipation stability |
· Aluminum-based core materials have a large heat capacity and uniform temperature distribution (temperature difference ≤5℃). · There is no thermal aggregation phenomenon, which extends the service life of PCBA by more than 30% |
Outdoor industrial control equipment, automotive-grade LED vehicle lamps, fast-charging heads for consumer electronics (no faults during long-term high-load operation) | |||
| Mechanical strength and warpage resistance |
· The aluminum substrate has strong rigidity and its impact/vibration resistance is superior to that of FR-4 · The flatness after high-temperature welding is ≤0.1mm/m (far superior to 0.3mm/m of FR-4). |
Automotive-grade in-vehicle PCBA (adapted to driving vibration), precision components for medical equipment (avoiding signal distortion caused by assembly gaps) | |||
| Environmental protection and compliance |
· The aluminum core material is recyclable and complies with RoHS/REACH standards · Halogen-free insulation layer is optional, with low volatility and low EMI |
Medical-grade PCBA (ISO 13485 compliant), consumer electronics export products (meeting environmental protection requirements in Europe and America) | |||
| Advantages of integrated design |
· It can replace the combination of "FR-4 substrate + heat sink", reducing the PCBA assembly process by 30% · It supports an integrated design of high-density wiring and heat dissipation Windows |
Thin consumer electronics products , compact industrial control modules (saving installation space) | |||
| Reliability and stability |
· Operating temperature range: -40 to 125℃ · The insulation resistance is ≥10¹⁰Ω, the breakdown voltage is ≥2kV, and it has strong surge resistance |
Automotive-grade AEC-Q200 certified products, industrial control equipment for extreme environments |
Manufacturing Capabilities
| PCB Manufacturing Capability | |||||
| ltem | Production capability | Min space for S/M to pad, to SMT | 0.075mm/0.1mm | Homogeneity of Plating Cu | z90% |
| Layer Count | 1~40 | Min space for legend to pad/ to SMT | 0.2mm/0.2mm | Accuracy of pattern to pattern | ±3mil(±0.075mm) |
| Production size(Min & Max) | 250mmx40mm/710mmx250mm | Surface treatment thickness for Ni/Au/Sn/OSP | 1~6um /0.05~0.76um /4~20um/ 1um | Accuracy of pattern to hole | ±4mil (±0.1mm ) |
| Copper thickness of lamination | 1/3 ~ 10z | Min size E- tested pad | 8 X 8mil | Min line width/space | 0.045 /0.045 |
| Product board thickness | 0.036~2.5mm | Min space between tested pads | 8mil | Etching tolerance | +20%0.02mm) |
| Auto-cutting accuracy | 0.1mm | Min dimention tolerance of outline (outside edge to circuit) | ±0.1mm | Cover layer alignment tolerance | ±6mil (±0.1 mm) |
| Drill size(Min/Max/hole sizetolerance) | 0.075mm/6.5mm/±0.025mm | Min dimention tolerance of outline | ±0.1mm | Excessive adhesive tolerancefor pressing C/L | 0.1mm |
| Min percent for CNC slot length and width | ≤0.5% | Min R corner radius of outline(inner filleted corner) | 0.2mm | Alignment tolerance forthermosetting S/M and UV S/M | ±0.3mm |
| maximum aspect Ratio(thickness/hole diameter) | 8:1 | Min space golden finger to outline | 0.075mm | Min S/M bridge | 0.1mm |

Common questions about aluminum pcb board lamination
Q1.What are the differences between the aluminum pcb board stack structure and the standard PCB?
A:The aluminum-based PCB stack structure uses an aluminum core and, compared with the traditional FR4 PCB, has superior thermal conductivity. This makes it an ideal choice for applications that require efficient heat dissipation.
Q2. Can multi-layer aluminum circuit board maintain high signal integrity?
A:The answer is affirmative, as long as the design is appropriate. Although the aluminum layer may affect signal propagation, reasonable stacking structure planning, material selection and layout techniques can ensure high signal integrity in multi-layer designs.
Q3. How does the thickness of the aluminum core affect the performance of a PCB?
A:Thicker aluminum cores usually can enhance heat dissipation efficiency through better heat dissipation performance. However, it will also increase weight and may increase manufacturing complexity, so the thickness must be balanced with other design requirements.
Q4. Is the aluminum circuit board stack structure suitable for all types of electronic designs?
A:Although aluminum printed circuit boards stack structures perform well in applications with high power and high heat dissipation requirements, not all designs need or adopt them economically. They have the greatest advantages in scenarios where heat dissipation management is of critical importance.
Q5. How to solve the thermal expansion difference in the laminated structure of aluminum printed circuit boards?
A:Careful selection of materials, appropriate layer thickness and ingenious use of vias can help control differences in thermal expansion. Some designs also incorporate stress relief structures to minimize the impact of thermal cycling.